Single dose pharmacokinetics of the transdermal rotigotine patch in patients with impaired renal function
- PMID: 21707699
- PMCID: PMC3248255
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04053.x
Single dose pharmacokinetics of the transdermal rotigotine patch in patients with impaired renal function
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the influence of different stages of chronic renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics and safety/tolerability of the transdermally applied dopamine agonist rotigotine in an open label group comparison including 32 subjects (healthy, mild, moderate or severe impairment of renal function and patients with end-stage renal insufficiency requiring haemodialysis). METHODS All subjects received a single transdermal 10 cm² patch (24 h patch-on period) containing 4.5 mg rotigotine (nominal drug release 2 mg 24 h⁻¹). Main evaluations included relative bioavailability and renal elimination of rotigotine and its metabolites.
Results: Point estimates for the ratios between the groups with moderate to severe renal impairment and healthy subjects for the pharmacokinetic parameters AUC(0,t(last) ) and C(max) for the active substance unconjugated rotigotine were near 1:0.88 for AUC and 0.93 for C(max) for moderate renal impairment, 1.14 and 1.18 for severe renal impairment and 1.05 and 1.25 for end-stage renal insufficiency requiring haemodialysis. There was no correlation of these parameters with creatinine clearance. The amount of unconjugated rotigotine excreted into urine and renal clearance decreased with increasing severity of renal insufficiency but had no observable effect on total clearance as the amounts excreted were below 1% of the administered dose. Occurrence of adverse events did not increase with the degree of renal insufficiency.
Conclusions: The pharmacokinetic profiles of unconjugated rotigotine were similar in healthy subjects and subjects with impaired renal function indicating that no dose adjustments are required for transdermal rotigotine in patients with different stages of chronic renal insufficiency including patients on haemodialysis.
© 2011 UCB Biosciences GmbH. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
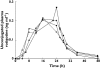
 group 5 end-stage renal impairment
group 5 end-stage renal impairment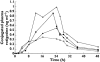
 group 5 end-stage renal impairment
group 5 end-stage renal impairmentReferences
-
- Pfeiffer RF. A promising new technology for Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2005;65(Suppl 1):S6–10. - PubMed
-
- Chase TN. The significance of continuous dopaminergic stimulation in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Drugs. 1998;55(Suppl 1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Cawello W, Wolff HM, Meuling WJA, Horstmann R, Braun M. Transdermal administration of radiolabelled [14C]-rotigotine by a patch formulation. A mass balance trial. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46:851–7. - PubMed
-
- Cawello W, Braun M, Boekens H. Absorption, disposition, metabolic fate, and elimination of the dopamine agonist rotigotine in man – administration by intravenous infusion or transdermal delivery. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37:2055–60. - PubMed
-
- Braun M, Cawello W, Andreas J-O, Boekens H, Horstmann R. Lack of pharmacokinetic interactions between transdermal rotigotine and oral levodopa/carbidopa. J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;49:1047–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

