Expression of hedgehog pathway components in prostate carcinoma microenvironment: shifting the balance towards autocrine signalling
- PMID: 21707705
- PMCID: PMC4934422
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03860.x
Expression of hedgehog pathway components in prostate carcinoma microenvironment: shifting the balance towards autocrine signalling
Abstract
Aims: The hedgehog (Hh) signalling pathway has been implicated in the pathogenesis and aggressiveness of prostate cancer through epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. The aim of this study was to elucidate the cell-type partitioned expression of the Hh pathway biomarkers in the non-neoplastic and tumour microenvironments and to correlate it with the grade and stage of prostate cancer.
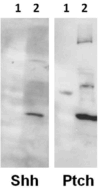
Methods and results: Expression of the Hh pathway components (Shh, Smo, Ptch, Gli1) in the microenvironment of non-neoplastic peripheral zone (n = 119), hormone-naive primary prostate carcinoma (n = 141) and castrate-resistant bone marrow metastases (n = 53) was analysed using immunohistochemistry in tissue microarrays and bone marrow sections. Results showed that epithelial Shh, Smo and Ptch expression was up-regulated, whereas stromal Smo, Ptch, and Gli1 expression was down-regulated in prostate carcinomas compared to non-neoplastic peripheral zone tissue. Ptch expression was modulated further in high-grade and high-stage primary tumours and in bone marrow metastases. Hh signalling correlated with ki67 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) but not with CD31 expression.
Conclusion: Our results highlight the importance of Hh-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the non-neoplastic prostate and imply that shifting the balance from paracrine towards autocrine signalling is important in the pathogenesis and progression of prostate carcinoma.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Limited.
Figures

References
-
- Teglund S, Toftgård R. Hedgehog beyond medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:181–208. - PubMed
-
- Azoulay S, Terry S, Chimingqi M, et al. Comparative expression of Hedgehog ligands at different stages of prostate carcinoma progression. J Pathol. 2008;216:460–470. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MM., Jr The hedgehog signaling network. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;123A:5–28. - PubMed
-
- Marker PC. Does prostate cancer co-opt the developmental program? Differentiation. 2008;76:736–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

