Antibodies toward infliximab are associated with low infliximab concentration at treatment initiation and poor infliximab maintenance in rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 21708018
- PMCID: PMC3218920
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3386
Antibodies toward infliximab are associated with low infliximab concentration at treatment initiation and poor infliximab maintenance in rheumatic diseases
Abstract
Introduction: A proportion of patients receiving infliximab have antibodies toward infliximab (ATI), which are associated with increased risk of infusion reaction and reduced response to treatment. We studied the association of infliximab concentration at treatment initiation and development of ATI as well as the association of the presence of ATI and maintenance of infliximab.
Methods: All patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or spondyloarthritis (SpA) receiving infliximab beginning in December 2005 were retrospectively followed until January 2009 or until infliximab discontinuation. Trough serum infliximab and ATI concentrations were measured at each visit. The patients were separated into two groups: ATI(pos) if ATI were detected at least once during the follow-up period and ATI(neg) otherwise. Repeated measures analysis of variance was used to study the association of infliximab concentration at treatment initiation and the development of ATI. Maintenance of infliximab in the two groups was studied by using Kaplan-Meier curves.
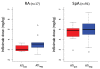
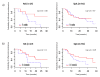
Results: We included 108 patients: 17 with RA and 91 with SpA. ATI were detected in 21 patients (19%). The median time to ATI detection after initiation of infliximab was 3.7 months (1.7 to 26.0 months). For both RA and SpA patients, trough infliximab concentration during the initiation period was significantly lower for ATI(pos) than ATI(neg) patients. RA patients showed maintenance of infliximab at a median of 19.5 months (5.0 to 31.0 months) and 12.0 months (2.0 to 24.0 months) for ATI(neg) and ATI(pos) groups, respectively (P = 0.08). SpA patients showed infliximab maintenance at a median of 16.0 months (3.0 to 34.0 months) and 9.5 months (3.0 to 39.0 months) for ATI(neg) and ATI(pos) groups, respectively (P = 0.20). Among SpA patients, those who were being treated concomitantly with methotrexate had a lower risk of developing ATI than patients not taking methotrexate (0 of 14 patients (0%) vs. 25 of 77 patients (32%); P = 0.03).
Conclusions: High concentrations of infliximab during treatment initiation reduce the development of ATI, and the absence of ATI may be associated with prolonged maintenance of infliximab. Thus, trough serum infliximab concentration should be monitored early in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Figures

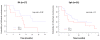
Comment in
-
Are we ready for therapeutic drug monitoring of biologic therapeutics?Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Aug 2;13(4):120. doi: 10.1186/ar3395. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21861867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maini RN, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Davis D, Macfarlane JD, Antoni C, Leeb B, Elliott MJ, Woody JN, Schaible TF, Feldmann M. Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1552–1563. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1552::AID-ART5>3.0.CO;2-W. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Zink A, Alten R, Burmester G, Golder W, Gromnica-Ihle E, Kellner H, Schneider M, Sörensen H, Zeidler H, Reddig J, Sieper J. Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: an open, observational, extension study of a three-month, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2224–2233. doi: 10.1002/art.11104. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, Sieper J, DeWoody K, Williamson P, Braun J. Ankylosing Spondylitis Study for the Evaluation of Recombinant Infliximab Therapy Study Group. Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT) Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:582–591. doi: 10.1002/art.20852. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bendtzen K, Geborek P, Svenson M, Larsson L, Kapetanovic MC, Saxne T. Individualized monitoring of drug bioavailability and immunogenicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3782–3789. doi: 10.1002/art.22214. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

