Impairment of adult hippocampal neural progenitor proliferation by methamphetamine: role for nitrotyrosination
- PMID: 21708025
- PMCID: PMC3142219
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-4-28
Impairment of adult hippocampal neural progenitor proliferation by methamphetamine: role for nitrotyrosination
Abstract
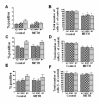
Methamphetamine (METH) abuse has reached epidemic proportions, and it has become increasingly recognized that abusers suffer from a wide range of neurocognitive deficits. Much previous work has focused on the deleterious effects of METH on mature neurons, but little is known about the effects of METH on neural progenitor cells (NPCs). It is now well established that new neurons are continuously generated from NPCs in the adult hippocampus, and accumulating evidence suggests important roles for these neurons in hippocampal-dependent cognitive functions. In a rat hippocampal NPC culture system, we find that METH results in a dose-dependent reduction of NPC proliferation, and higher concentrations of METH impair NPC survival. NPC differentiation, however, is not affected by METH, suggesting cell-stage specificity of the effects of METH. We demonstrate that the effects of METH on NPCs are, in part, mediated through oxidative and nitrosative stress. Further, we identify seventeen NPC proteins that are post-translationally modified via 3-nitrotyrosination in response to METH, using mass spectrometric approaches. One such protein was pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2), an important mediator of cellular energetics and proliferation. We identify sites of PKM2 that undergo nitrotyrosination, and demonstrate that nitration of the protein impairs its activity. Thus, METH abuse may result in impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and effects on NPCs may be mediated by protein nitration. Our study has implications for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for METH-abusing individuals with neurologic dysfunction and may be applicable to other neurodegenerative diseases in which hippocampal neurogenesis is impaired.
Figures



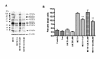


Similar articles
-
Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of proliferation of adult rat hippocampal progenitor cells in vitro.J Pineal Res. 2015 May;58(4):418-28. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12225. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 25752339
-
Mitochondrial fragmentation is involved in methamphetamine-induced cell death in rat hippocampal neural progenitor cells.PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005546. Epub 2009 May 14. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19436752 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine increases HIV infectivity in neural progenitor cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 5;293(1):296-311. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000795. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29158267 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity: role of peroxynitrite and neuroprotective role of antioxidants and peroxynitrite decomposition catalysts.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;939:366-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03646.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11462792 Review.
-
The role of hippocampal adult neurogenesis in methamphetamine addiction.Brain Plast. 2018 Aug 10;3(2):157-168. doi: 10.3233/BPL-170058. Brain Plast. 2018. PMID: 30151340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic administration of amphetamines disturbs development of neural progenitor cells in young adult nonhuman primates.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Jul 13;85:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.03.023. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29601895 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of PKM2 in Multiple Signaling Pathways Related to Neurological Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):5002-5026. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03901-y. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38157121 Review.
-
Changes in metabolic proteins in ex vivo rat retina during glutamate-induced neural progenitor cell induction.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):177-84. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2769-z. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27421851
-
Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 impairs cognition in systemic lupus erythematosus by promoting microglial synaptic pruning via the β-catenin signaling pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Oct 13;18(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02279-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34645459 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Fractional Anisotropy in the Gray Matter of Amygdala-Hippocampus-Nucleus Accumbens Circuit in Methamphetamine Users: an In Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study.Neurotox Res. 2018 May;33(4):801-811. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9828-4. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29038922
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

