Renal function at the time of a myocardial infarction maintains prognostic value for more than 10 years
- PMID: 21708030
- PMCID: PMC3141759
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-11-37
Renal function at the time of a myocardial infarction maintains prognostic value for more than 10 years
Abstract
Background: Renal function is an important predictor of mortality in patients with myocardial infarction (MI), but changes in the impact over time have not been well described.We examined the importance of renal function by estimated GFR (eGFR) and se-creatinine as an independent long-term prognostic factor.
Methods: Prospective follow-up of 6653 consecutive MI patients screened for entry in the Trandolapril Cardiac Evaluation (TRACE) study. The patients were analysed by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, landmark analysis and Cox proportional hazard models. Outcome measure was all-cause mortality.
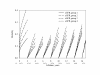
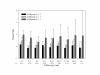
Results: An eGFR below 60 ml per minute per 1.73 m2, consistent with chronic renal disease, was present in 42% of the patients. We divided the patients into 4 groups according to eGFR. Overall, Cox proportional-hazards models showed that eGFR was a significant prognostic factor in the two groups with the lowest eGFR, hazard ratio 1,72 (confidence interval (CI) 1,56-1,91) in the group with the lowest eGFR. Using the eGFR group with normal renal function as reference, we observed an incremental rise in hazard ratio. We divided the follow-up period in 2-year intervals. Landmark analysis showed that eGFR at the time of screening continued to show prognostic effect until 16 years of follow-up. By multivariable Cox regression analysis, the prognostic effect of eGFR persisted for 12 years and of se-creatinine for 10 years. When comparing the lowest group of eGFR with the group with normal eGFR, prognostic significance was present in the entire period of follow-up with a hazard ratio between 1,97 (CI 1,65-2,35) and 1,35 (CI 0,99-1,84) in the 2-year periods.
Conclusions: One estimate of renal function is a strong and independent long-term prognostic factor for 10-12 years following a MI.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diabetes is an independent predictor of survival 17 years after myocardial infarction: follow-up of the TRACE registry.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010 Jun 2;9:22. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-22. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010. PMID: 20525192 Free PMC article.
-
Dipstick proteinuria as a surrogate marker of long-term mortality after acute myocardial infarction.J Cardiol. 2013 Nov;62(5):277-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23806546
-
Kidney Function as Risk Factor and Predictor of Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Among Older Adults.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Mar;77(3):386-396.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.015. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33197533
-
GFR and cardiovascular outcomes after acute myocardial infarction: results from the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry.Am J Kidney Dis. 2012 Jun;59(6):795-802. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.01.016. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012. PMID: 22445708
-
Declining renal function after myocardial infarction predicts poorer long-term outcome.Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010 Apr;17(2):181-6. doi: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e328332d48b. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010. PMID: 19829117
Cited by
-
Impact of Comorbid Disease Burden on Clinical Outcomes of Female Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients.Chonnam Med J. 2023 Jan;59(1):61-69. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2023.59.1.61. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Chonnam Med J. 2023. PMID: 36794246 Free PMC article.
-
The Seattle Post Myocardial Infarction Model (SPIM): prediction of mortality after acute myocardial infarction with left ventricular dysfunction.Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2014 Mar;3(1):46-55. doi: 10.1177/2048872613502283. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2014. PMID: 24562803 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The dose-response association between estimated glomerular filtration rate and prognosis of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction from rural areas of China's Liaoning province.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(52):e9508. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009508. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29384954 Free PMC article.
-
What Are the Causes of Death among Patients Admitted to a Contemporary Tertiary-Level Cardiology Department? An Analysis of 10 Years of Morbidity and Mortality Meetings.Pathophysiology. 2023 Sep 30;30(4):467-479. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology30040034. Pathophysiology. 2023. PMID: 37873854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9(12 Suppl):S16–23. - PubMed
-
- Luft FC. Renal disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Basic Res Cardiol. 2000;95(Suppl 1):I72–76. - PubMed
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS. Cardiovascular disease and chronic renal disease: a new paradigm. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35(4 Suppl 1):S117–131. - PubMed
-
- Hillege HL, Nitsch D, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, McMurray JJ, Yusuf S, Granger CB, Michelson EL, Ostergren J, Cornel JH. et al.Renal function as a predictor of outcome in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure. Circulation. 2006;113(5):671–678. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.580506. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

