The role of trigeminal interpolaris-caudalis transition zone in persistent orofacial pain
- PMID: 21708312
- PMCID: PMC3257052
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385198-7.00008-4
The role of trigeminal interpolaris-caudalis transition zone in persistent orofacial pain
Abstract
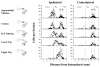
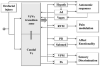
Previous studies have established the role of the medullary dorsal horn or the subnucleus caudalis of the spinal trigeminal complex, a homolog of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, in trigeminal pain processing. In addition to the medullary dorsal horn, recent studies have pointed out increased excitability and sensitization of trigeminal interpolaris and caudalis transition zone (Vi/Vc) following deep orofacial injury, involving neuron-glia-cytokine interactions. The Vi/Vc transition zone accesses rostral brain regions that are important for descending pain modulation, and somatovisceral and somatoautonomic processing and plays a unique role in coordinating trigeminal nocifensive responses.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential involvement of trigeminal transition zone and laminated subnucleus caudalis in orofacial deep and cutaneous hyperalgesia: the effects of interleukin-10 and glial inhibitors.Mol Pain. 2009 Dec 21;5:75. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-75. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 20025765 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem mechanisms of persistent pain following injury.J Orofac Pain. 2004 Fall;18(4):299-305. J Orofac Pain. 2004. PMID: 15636012
-
Selective distribution and function of primary afferent nociceptive inputs from deep muscle tissue to the brainstem trigeminal transition zone.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Sep 20;498(3):390-402. doi: 10.1002/cne.21062. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16871539
-
Central nervous system plasticity and persistent pain.J Orofac Pain. 1999 Summer;13(3):155-63; discussion 164-71. J Orofac Pain. 1999. PMID: 10823030 Review.
-
Non-neuronal cells act as crucial players in neuropathic orofacial pain.J Oral Biosci. 2024 Sep;66(3):491-495. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Oral Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39032826 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory actions of borneol on the substantia gelatinosa neurons of the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis in mice.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 1;24(5):433-440. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.5.433. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32830150 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the excitability of small-diameter trigeminal ganglion neurons projecting to the trigeminal nucleus interpolaris/caudalis transition zone following masseter muscle inflammation.Mol Pain. 2013 Sep 30;9:49. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-49. Mol Pain. 2013. PMID: 24073832 Free PMC article.
-
Method for cryopreservation of brainstem pons and medulla oblongata tissue from Sprague Dawley rats for establishing primary mixed neuron-glia cell cultures.Brain Res. 2025 Aug 1;1860:149665. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149665. Epub 2025 May 1. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40318759
-
Molecular Segmentation of the Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus in the Adult Mouse Brain.Front Neuroanat. 2021 Dec 10;15:785840. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2021.785840. eCollection 2021. Front Neuroanat. 2021. PMID: 34955765 Free PMC article.
-
Role of medullary astroglial glutamine synthesis in tooth pulp hypersensitivity associated with frequent masseter muscle contraction.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918763270. doi: 10.1177/1744806918763270. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 29448913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvidsson J, Pfaller K, Gmeiner S. The ganglionic origins and central projections of primary sensory neurons innervating the upper and lower lips in the rat Somatosens. Mot. Res. 1992;9:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson J, Raappana P. An HRP study of the central projections from primary sensory neurons innervating the rat masseter muscle. Brain Res. 1989;480:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum AI, Ralston DD, Ralston HJ., 3rd Bulbospinal projections in the primate: a light and electron microscopic study of a pain modulating system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986;250:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Beitz AJ. The nuclei of origin of brainstem serotonergic projections to the rodent spinal trigeminal nucleus. Neurosci. Lett. 1982;32:223–228. - PubMed
-
- Beitz AJ, Clements JR, Ecklund LJ, Mullett MM. The nuclei of origin of brainstem enkephalin and cholecystokinin projections to the spinal trigeminal nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience. 1987;20:409–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

