Nutrient-enhanced diet reduces noise-induced damage to the inner ear and hearing loss
- PMID: 21708355
- PMCID: PMC3132794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.02.006
Nutrient-enhanced diet reduces noise-induced damage to the inner ear and hearing loss
Abstract
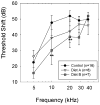
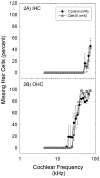
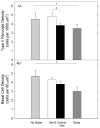
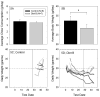
Oxidative stress has been implicated broadly as a cause of cell death and neural degeneration in multiple disease conditions; however, the evidence for successful intervention with dietary antioxidant manipulations has been mixed. In this study, we investigated the potential for protection of cells in the inner ear using a dietary supplement with multiple antioxidant components, which were selected for their potential interactive effectiveness. Protection against permanent threshold shift (PTS) was observed in CBA/J mice maintained on a diet supplemented with a combination of β-carotene, vitamins C and E, and magnesium when compared with PTS in control mice maintained on a nutritionally complete control diet. Although hair cell survival was not enhanced, noise-induced loss of type II fibrocytes in the lateral wall was significantly reduced (P < 0.05), and there was a trend toward less noise-induced loss in strial cell density in animals maintained on the supplemented diet. Taken together, our data suggest that prenoise oral treatment with the high-nutrient diet can protect cells in the inner ear and reduce PTS in mice. The demonstration of functional and morphologic preservation of cells in the inner ear with oral administration of this antioxidant supplemented diet supports the possibility of translation to human patients and suggests an opportunity to evaluate antioxidant protection in mouse models of oxidative stress-related disease and pathology.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kim J, Lee HJ, Lee KW. Naturally occurring phytochemicals for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2010 Mar;112(6):1415–30. - PubMed
-
- Rottkamp CA, Nunomura A, Hirai K, Sayre LM, Perry G, Smith MA. Will antioxidants fulfill their expectations for the treatment of Alzheimer disease? Mech Ageing Dev. 2000 Jul 31;116(2–3):169–79. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Therapeutic approaches to mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009 Dec;15( Suppl 3):S189–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

