Proteomic biomarkers apolipoprotein A1, truncated transthyretin and connective tissue activating protein III enhance the sensitivity of CA125 for detecting early stage epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 21708402
- PMCID: PMC3152646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.06.002
Proteomic biomarkers apolipoprotein A1, truncated transthyretin and connective tissue activating protein III enhance the sensitivity of CA125 for detecting early stage epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
Objective: The low prevalence of ovarian cancer demands both high sensitivity (>75%) and specificity (99.6%) to achieve a positive predictive value of 10% for successful early detection. Utilizing a two stage strategy where serum marker(s) prompt the performance of transvaginal sonography (TVS) in a limited number (2%) of women could reduce the requisite specificity for serum markers to 98%. We have attempted to improve sensitivity by combining CA125 with proteomic markers.
Methods: Sera from 41 patients with early stage (I/II) and 51 with late stage (III/IV) epithelial ovarian cancer, 40 with benign disease and 99 healthy individuals, were analyzed to measure 7 proteins [Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo-A1), truncated transthyretin (TT), transferrin, hepcidin, ß-2-microglobulin (ß2M), Connective Tissue Activating Protein III (CTAPIII), and Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 (ITIH4)]. Statistical models were fit by logistic regression, followed by optimization of factors retained in the models determined by optimizing the Akaike Information Criterion. A validation set included 136 stage I ovarian cancers, 140 benign pelvic masses and 174 healthy controls.
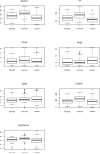
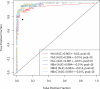
Results: In a training set analysis, the 3 most effective biomarkers (Apo-A1, TT and CTAPIII) exhibited 54% sensitivity at 98% specificity, CA125 alone produced 68% sensitivity and the combination increased sensitivity to 88%. In a validation set, the marker panel plus CA125 produced a sensitivity of 84% at 98% specificity (P=0.015, McNemar's test).
Conclusion: Combining a panel of proteomic markers with CA125 could provide a first step in a sequential two-stage strategy with TVS for early detection of ovarian cancer.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Berek JS, Friedlander ML, Bast RC., Jr . Ovarian Cancer. In: Hong WK, Bast RC Jr, Hait W, Kufe D, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, Holland JF, Frei E III, editors. Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 8th Edition PMPH-USA; Shelton, CT: 2010. pp. 1344–1375.
-
- Bast RC, Jr, Klug TL, St. John E, Jenison E, Niloff JM, Lazarus H, Berkowitz RS, Leavitt T, Griffiths CT, Parker L, Zurawski VR, Jr, Knapp RC. A radioimmunoassay using a monoclonal antibody to monitor the course of epithelial ovarian cancer. New Engl J Med. 1983;309:883–887. - PubMed
-
- Rosen D, Wang L, Atkinson JN, Yu Y, Lu K, Diamandis EP, Hellstrom I, Mok SC, Liu J, Bast RC., Jr Potential markers that complement expression of CA 125 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;99:267–77. - PubMed
-
- Skates SJ, Xu FJ, Yu YH, Sjovall K, Einhorn N, Chang Y, et al. Toward an optimal algorithm for ovarian cancer screening with longitudinal tumor markers. Cancer. 1995;76(10 Suppl):2004–2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

