Insights into the role of elastin in vocal fold health and disease
- PMID: 21708449
- PMCID: PMC3190022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2011.05.003
Insights into the role of elastin in vocal fold health and disease
Abstract
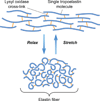
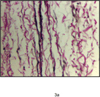
Elastic fibers are large, complex, and surprisingly poorly understood extracellular matrix macromolecules. The elastin fiber, generated from a single human gene--elastin, is a self assembling integral protein that endows critical mechanical proprieties to elastic tissues and organs such as the skin, lungs, and arteries. The biology of elastic fibers is complex because they have multiple components, a tightly regulated developmental deposition, a multistep hierarchical assembly, and unique biomechanical functions. Elastin is present in vocal folds, where it plays a pivotal role in the quality of phonation. This review article provides an overview of the genesis of elastin and its wide-ranging structure and function. Specific distribution within the vocal fold lamina propria across the lifespan in normal and pathological states and its contribution to vocal fold biomechanics will be examined. Elastin and elastin-derived molecules are increasingly investigated for their application in tissue engineering. The properties of various elastin-based materials will be discussed and their current and future applications evaluated. A new level of understanding of the biomechanical properties of vocal fold elastin composites and their molecular basis should lead to new strategies for elastic fiber repair and regeneration in aging and disease.
Copyright © 2012 The Voice Foundation. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insights Into the Role of Collagen in Vocal Fold Health and Disease.J Voice. 2017 Sep;31(5):520-527. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.01.008. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Voice. 2017. PMID: 28359643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for heterozygous abnormalities of the elastin gene (ELN) affecting the quantity of vocal fold elastic fibers: a pilot study.J Voice. 2011 Mar;25(2):e85-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2010.04.006. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Voice. 2011. PMID: 20926252 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile fiber-reinforced hydrogels to mimic the microstructure and mechanics of human vocal-fold upper layers.Acta Biomater. 2023 Dec;172:92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.09.035. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37748548
-
Biomechanical and histologic observations of vocal fold fibrous proteins.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000 Jan;109(1):77-85. doi: 10.1177/000348940010900115. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000. PMID: 10651418
-
Mechanical characterization of vocal fold tissue: a review study.J Voice. 2014 Nov;28(6):657-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Jul 5. J Voice. 2014. PMID: 25008382 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating the behaviors of mesenchymal stem cells via the combination of high-frequency vibratory stimulations and fibrous scaffolds.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013 Aug;19(15-16):1862-78. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0694. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013. PMID: 23516973 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the anti-inflammatory potential of topical hyaluronic acid for vocal fold injury in a rat model.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jan;281(1):301-310. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08278-1. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 37823895 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear viscoelastic characterization of human vocal fold tissues under large-amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS).J Rheol (N Y N Y). 2018 May;62(3):695-712. doi: 10.1122/1.4996320. Epub 2018 Apr 1. J Rheol (N Y N Y). 2018. PMID: 29780189 Free PMC article.
-
Study of extracellular matrix in vocal fold biomechanics using a two-phase model.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2015 Jan;14(1):49-57. doi: 10.1007/s10237-014-0585-5. Epub 2014 May 3. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2015. PMID: 24792897 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Determinants of Hoarseness in School-Aged Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 30;19(9):5468. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095468. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hahn MS, Kobler JB, Starcher BC, Zeitels SM, Langer R. Quantitative and comparative studies of the vocal fold extracellular matrix: elastic fibers and hyaluronic acid. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2006;115(2):156–164. - PubMed
-
- Hammond TH, Zhou R, Hammond EH, Pawlak A, Gray SD. The intermediate layer: a morphologic study of the elastin and hyaluronic acid constituents of normal human vocal folds. J Voice. 1997;11(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Gray SD, Chan KJ, Turner B. Dissection plane of the human vocal fold lamina propria and elastin fibre concentration. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000;120:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular Biology of The Cell. 5th ed. New York: Garland Publishing; 2008.
-
- Tassabehji M, Metcalfe K, Donnai D, Hurst J, Reardon W, Burch M, Read P. Elastin: genomic structure and point mutations in patients with supravalvular aortic stenosis. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6(7):1029–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

