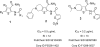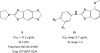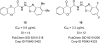High throughput screening of a library based on kinase inhibitor scaffolds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv
- PMID: 21708485
- PMCID: PMC3183257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.05.005
High throughput screening of a library based on kinase inhibitor scaffolds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv
Abstract
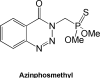
Kinase targets are being pursued in a variety of diseases beyond cancer, including immune and metabolic as well as viral, parasitic, fungal and bacterial. In particular, there is a relatively recent interest in kinase and ATP-binding targets in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in order to identify inhibitors and potential drugs for essential proteins that are not targeted by current drug regimens. Herein, we report the high throughput screening results for a targeted library of approximately 26,000 compounds that was designed based on current kinase inhibitor scaffolds and known kinase binding sites. The phenotypic data presented herein may form the basis for selecting scaffolds/compounds for further enzymatic screens against specific kinase or other ATP-binding targets in Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on the apparent activity against the whole bacteria in vitro.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ananthan S, Faaleolea ER, Goldman RC, Hobrath JV, Kwong CD, Laughon BE, Maddry JA, Mehta A, Rasmussen L, Reynolds RC, Secrist JA, III, Shindo N, Showe DN, Sosa MI, Suling WJ, White EL. High-throughput screening for inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2009;89:334–353. doi: 10.1016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vieth M, Sutherland JJ, Robertson DH, Campbell RM. Kinomics: characterizing the therapeutically validated kinase space. Drug Discov Today. 2005 Jun 15;10:839–846. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:28–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources