Changes in patient characteristics in anti-tumour necrosis factor clinical trials for rheumatoid arthritis: results of an analysis of the literature over the past 16 years
- PMID: 21708910
- PMCID: PMC3147244
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.146043
Changes in patient characteristics in anti-tumour necrosis factor clinical trials for rheumatoid arthritis: results of an analysis of the literature over the past 16 years
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate changes in baseline patient characteristics and entry criteria of randomised, controlled studies of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
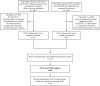
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed using predefined inclusion criteria to identify randomised, double-blind, controlled trials that evaluated TNFα inhibitors in adult RA patients. Entry criteria and baseline clinical characteristics were evaluated over time for methotrexate-experienced and methotrexate-naive study populations. Enrolment start date for each trial was the time metric. The anchor time was the study with the earliest identifiable enrolment start date.
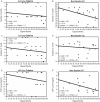
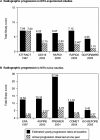
Results: 44 primary publications (reporting the primary study endpoint) from 1993 to 2008 met the inclusion criteria. Enrolment start dates of August 1993 and May 1997 were identified as time anchors for the 37 methotrexate-experienced studies and the seven methotrexate-naive studies, respectively. In methotrexate-experienced trials, no significant change was observed over the years included in this study in any inclusion criteria (including swollen joint counts and C-reactive protein (CRP)), but a significant decrease over time was observed in the baseline swollen joint count, CRP and total Sharp or van der Heijde modified Sharp score, but not in baseline tender joint counts. In the methotrexate-naive studies, significant decreases over the years were observed in swollen joint and tender joint inclusion criteria, but not in baseline tender joint count, baseline CRP, CRP inclusion criteria or baseline total Sharp or van der Heijde modified Sharp score.
Conclusion: Inclusion criteria and baseline characteristics of RA patients enrolled in studies of TNFα inhibitors have changed, with more recent trials enrolling cohorts with lower disease activity, especially in methotrexate-experienced trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wilske KR, Healey LA. Challenging the therapeutic pyramid: a new look at treatment strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl 1990;25:4–7 - PubMed
-
- Chu CQ, Field M, Feldmann M, et al. Localization of tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial tissues and at the cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1991;34:1125–32 - PubMed
-
- Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum 1993;36:1681–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

