Severe lung fibrosis requires an invasive fibroblast phenotype regulated by hyaluronan and CD44
- PMID: 21708929
- PMCID: PMC3135364
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20102510
Severe lung fibrosis requires an invasive fibroblast phenotype regulated by hyaluronan and CD44
Abstract
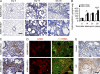
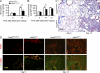
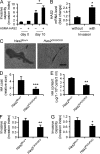
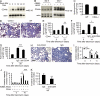
Tissue fibrosis is a major cause of morbidity, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a terminal illness characterized by unremitting matrix deposition in the lung. The mechanisms that control progressive fibrosis are unknown. Myofibroblasts accumulate at sites of tissue remodeling and produce extracellular matrix components such as collagen and hyaluronan (HA) that ultimately compromise organ function. We found that targeted overexpression of HAS2 (HA synthase 2) by myofibroblasts produced an aggressive phenotype leading to severe lung fibrosis and death after bleomycin-induced injury. Fibroblasts isolated from transgenic mice overexpressing HAS2 showed a greater capacity to invade matrix. Conditional deletion of HAS2 in mesenchymal cells abrogated the invasive fibroblast phenotype, impeded myofibroblast accumulation, and inhibited the development of lung fibrosis. Both the invasive phenotype and the progressive fibrosis were inhibited in the absence of CD44. Treatment with a blocking antibody to CD44 reduced lung fibrosis in mice in vivo. Finally, fibroblasts isolated from patients with IPF exhibited an invasive phenotype that was also dependent on HAS2 and CD44. Understanding the mechanisms leading to an invasive fibroblast phenotype could lead to novel approaches to the treatment of disorders characterized by severe tissue fibrosis.
Figures



References
-
- Ando H., Kubin T., Schaper W., Schaper J. 1999. Cardiac microvascular endothelial cells express alpha-smooth muscle actin and show low NOS III activity. Am. J. Physiol. 276:H1755–H1768 - PubMed
-
- ATS/ERS 2000. American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 161:646–664 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

