Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway mediated by p110α regulates invadopodia formation
- PMID: 21708979
- PMCID: PMC3216328
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201009126
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway mediated by p110α regulates invadopodia formation
Abstract
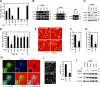
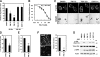
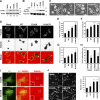
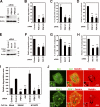
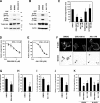
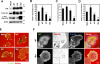
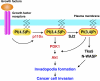
Invadopodia are extracellular matrix-degrading protrusions formed by invasive cancer cells that are thought to function in cancer invasion. Although many invadopodia components have been identified, signaling pathways that link extracellular stimuli to invadopodia formation remain largely unknown. We investigate the role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling during invadopodia formation. We find that in human breast cancer cells, both invadopodia formation and degradation of a gelatin matrix were blocked by treatment with PI3K inhibitors or sequestration of D-3 phosphoinositides. Functional analyses revealed that among the PI3K family proteins, the class I PI3K catalytic subunit p110α, a frequently mutated gene product in human cancers, was selectively involved in invadopodia formation. The expression of p110α with cancerous mutations promoted invadopodia-mediated invasive activity. Furthermore, knockdown or inhibition of PDK1 and Akt, downstream effectors of PI3K signaling, suppressed invadopodia formation induced by p110α mutants. These data suggest that PI3K signaling via p110α regulates invadopodia-mediated invasion of breast cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PI3K p110α/Akt signaling negatively regulates secretion of the intestinal peptide neurotensin through interference of granule transport.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Aug;26(8):1380-93. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1024. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22700584 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis of the focal adhesion to invadopodia transition identifies a PI3K-PKCα invasive signaling axis.Sci Signal. 2012 Sep 11;5(241):ra66. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002964. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22969158 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PI3K and AKT specific isoforms in ovarian cancer cell migration, invasion and proliferation through the p70S6K1 pathway.Cell Signal. 2006 Dec;18(12):2262-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.05.019. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16839745
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Human Disease Mediated by Oncogenic and Primary Immunodeficiency Mutations in Class IA Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00575. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review.Ann Med. 2014 Sep;46(6):372-83. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2014.912836. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Ann Med. 2014. PMID: 24897931 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of synaptojanin 2 5'-phosphatase activity by Src.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Nov-Dec;6(6):518-25. doi: 10.4161/cam.22139. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 23076136 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of breast cancer invasion by TIS21/BTG2/Pc3-Akt1-Sp1-Nox4 pathway targeting actin nucleators, mDia genes.Oncogene. 2016 Jan 7;35(1):83-93. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.64. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25798836
-
Lowered Expression of Tumor Suppressor Candidate MYO1C Stimulates Cell Proliferation, Suppresses Cell Adhesion and Activates AKT.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 7;11(10):e0164063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164063. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27716847 Free PMC article.
-
The Small GTPase ARF6 Activates PI3K in Melanoma to Induce a Prometastatic State.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;79(11):2892-2908. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3026. Epub 2019 May 2. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31048499 Free PMC article.
-
Palladin regulation of the actin structures needed for cancer invasion.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(1):29-35. doi: 10.4161/cam.28024. Epub 2013 Jan 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24525547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artym V.V., Zhang Y., Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F., Yamada K.M., Mueller S.C. 2006. Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res. 66:3034–3043 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2177 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnett S.F., Defeo-Jones D., Fu S., Hancock P.J., Haskell K.M., Jones R.E., Kahana J.A., Kral A.M., Leander K., Lee L.L., et al. 2005. Identification and characterization of pleckstrin-homology-domain-dependent and isoenzyme-specific Akt inhibitors. Biochem. J. 385:399–408 10.1042/BJ20041140 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

