PW1 gene/paternally expressed gene 3 (PW1/Peg3) identifies multiple adult stem and progenitor cell populations
- PMID: 21709251
- PMCID: PMC3136256
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1103873108
PW1 gene/paternally expressed gene 3 (PW1/Peg3) identifies multiple adult stem and progenitor cell populations
Abstract
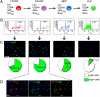
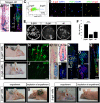
A variety of markers are invaluable for identifying and purifying stem/progenitor cells. Here we report the generation of a murine reporter line driven by Pw1 that reveals cycling and quiescent progenitor/stem cells in all adult tissues thus far examined, including the intestine, blood, testis, central nervous system, bone, skeletal muscle, and skin. Neurospheres generated from the adult PW1-reporter mouse show near 100% reporter-gene expression following a single passage. Furthermore, epidermal stem cells can be purified solely on the basis of reporter-gene expression. These cells are clonogenic, repopulate the epidermal stem-cell niches, and give rise to new hair follicles. Finally, we demonstrate that only PW1 reporter-expressing epidermal cells give rise to follicles that are capable of self-renewal following injury. Our data demonstrate that PW1 serves as an invaluable marker for competent self-renewing stem cells in a wide array of adult tissues, and the PW1-reporter mouse serves as a tool for rapid stem cell isolation and characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A patent has been filed for the Tg(
Figures


References
-
- Magavi SS, Leavitt BR, Macklis JD. Induction of neurogenesis in the neocortex of adult mice. Nature. 2000;405:951–955. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
-
- Jaks V, et al. Lgr5 marks cycling, yet long-lived, hair follicle stem cells. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1291–1299. - PubMed
-
- Relaix F, et al. Pw1, a novel zinc finger gene implicated in the myogenic and neuronal lineages. Dev Biol. 1996;177:383–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

