Establishing compliance with liquid medication administration in a child with autism
- PMID: 21709797
- PMCID: PMC3120077
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2011.44-381
Establishing compliance with liquid medication administration in a child with autism
Abstract
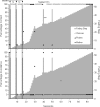
Children with autism often display difficulty with swallowing pills and liquid medications. In the current study, stimulus fading and positive reinforcement established compliance with liquid medication administration in a young boy with autism. The boy's mother eventually administered liquid medication on her own.
Keywords: autism; liquid medication; stimulus fading.
Figures
Similar articles
-
["I could see he was not acting like other children"].Soins Pediatr Pueric. 2014 Jan-Feb;(276):34-5. Soins Pediatr Pueric. 2014. PMID: 24617092 French.
-
[Treatment of a serious autistic disorder in a child with Naltrexone in an oral suspension form].Encephale. 2009 Apr;35(2):168-72. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19393386 French.
-
Further evaluation of response-independent delivery of preferred stimuli and child compliance.J Appl Behav Anal. 2011 Fall;44(3):665-9. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2011.44-665. J Appl Behav Anal. 2011. PMID: 21941401 Free PMC article.
-
[Psychopharmacology of autism].Encephale. 1996 May-Jun;22(3):197-203. Encephale. 1996. PMID: 8767048 Review. French.
-
Safety issues with drug therapies for autism spectrum disorders.J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66 Suppl 10:32-7. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16401148 Review.
Cited by
-
Difficulties experienced during preparation and administration of oral drugs.Turk Pediatri Ars. 2014 Sep 1;49(3):231-7. doi: 10.5152/tpa.2014.1795. eCollection 2014 Sep. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2014. PMID: 26078668 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies parents use to give children oral medicine: a qualitative study of online discussion forums.Scand J Prim Health Care. 2017 Jun;35(2):221-228. doi: 10.1080/02813432.2017.1333308. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2017. PMID: 28581890 Free PMC article.
-
Equity, acceptability and feasibility of using polyunsaturated fatty acids in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: a rapid systematic review.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Apr 16;18(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01354-8. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32299432 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptability, equity, and feasibility of using antipsychotics in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review.BMC Psychiatry. 2020 Nov 25;20(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02956-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33238921 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities for ABA intervention in Phelan-McDermid syndrome.Int J Dev Disabil. 2021 Mar 9;68(6):984-989. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2021.1895698. eCollection 2022. Int J Dev Disabil. 2021. PMID: 36816984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson O, Zweidorff O.K, Hjelde T, Rodland E.A. Sola legesenter: Problems when swallowing tablets. A questionnaire study from general practice. Tidsskrift for den Norske Laegeforening. 1995;115:947–949. - PubMed
-
- Ghuman J.K, Cataldo M.D, Beck M.H, Slifer K.J. Behavioral training for pill-swallowing difficulties in young children with autistic disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 2004;14:601–611. - PubMed
-
- Kerwin M.E. Empirically supported treatments in pediatric psychology: Severe feeding problems. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 1999;24:193–214. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

