Effect of particle size on the thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing metallic nanoparticles
- PMID: 21711761
- PMCID: PMC3211308
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-6-247
Effect of particle size on the thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing metallic nanoparticles
Abstract
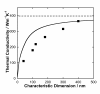
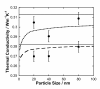
A one-parameter model is presented for the thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing dispersed metallic nanoparticles. The model takes into account the decrease in thermal conductivity of metal nanoparticles with decreasing size. Although literature data could be correlated well using the model, the effect of the size of the particles on the effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid could not be elucidated from these data. Therefore, new thermal conductivity measurements are reported for six nanofluids containing silver nanoparticles of different sizes and volume fractions. The results provide strong evidence that the decrease in the thermal conductivity of the solid with particle size must be considered when developing models for the thermal conductivity of nanofluids.
Figures
References
-
- Choi SUS, Zhang ZG, Yu W, Lockwood FE, Grulke EA. Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl Phys Lett. 2001;79:2252. doi: 10.1063/1.1408272. - DOI
-
- Eastman JA, Choi SUS, Li S, Yu W, Thompson W. Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett. 2001;78:718. doi: 10.1063/1.1341218. - DOI
-
- Kang HU, Kim SH, Oh JM. Estimation of thermal conductivity of nanofluid using experimental effective particle volume. Exp Heat Transfer. 2006;19:181. doi: 10.1080/08916150600619281. - DOI
-
- Patel HE, Das SK, Sundararajan T, Nair AS, George B, Pradeep T. Thermal conductivity of naked and monolayer protected metal nanoparticles based nanofluids: manifestation of anomalous enhancement and chemical effects. Appl Phys Lett. 2003;83:2931. doi: 10.1063/1.1602578. - DOI
-
- Xuan Y, Li Q. Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2000;21:58. doi: 10.1016/S0142-727X(99)00067-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

