Role of dendritic cells in the induction of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 21711933
- PMCID: PMC3125210
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-3701-1-20
Role of dendritic cells in the induction of regulatory T cells
Abstract
Dendritic cells (DCs) play a key role in initiating immune responses and maintaining immune tolerance. In addition to playing a role in thymic selection, DCs play an active role in tolerance under steady state conditions through several mechanisms which are dependent on IL-10, TGF-β, retinoic acid, indoleamine-2,3,-dioxygenase along with vitamin D. Several of these mechanisms are employed by DCs in induction of regulatory T cells which are comprised of Tr1 regulatory T cells, natural and inducible foxp3+ regulatory T cells, Th3 regulatory T cells and double negative regulatory T cells. It appears that certain DC subsets are highly specialized in inducing regulatory T cell differentiation and in some tissues the local microenvironment plays a role in driving DCs towards a tolerogenic response. In this review we discuss the recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms underlying DC driven regulatory T cell induction.
Figures
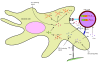
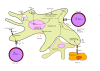
References
-
- Apetoh L, Quintana FJ, Pot C, Joller N, Xiao S, Kumar D, Burns EJ, Sherr DH, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with c-Maf to promote the differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells induced by IL-27. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:854–861. doi: 10.1038/ni.1912. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

