HIF induces human embryonic stem cell markers in cancer cells
- PMID: 21712410
- PMCID: PMC3129496
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3320
HIF induces human embryonic stem cell markers in cancer cells
Abstract
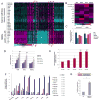
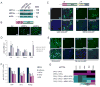
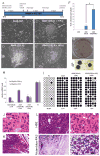
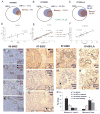
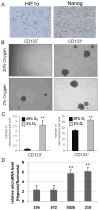
Low oxygen levels have been shown to promote self-renewal in many stem cells. In tumors, hypoxia is associated with aggressive disease course and poor clinical outcomes. Furthermore, many aggressive tumors have been shown to display gene expression signatures characteristic of human embryonic stem cells (hESC). We now tested whether hypoxia might be responsible for the hESC signature observed in aggressive tumors. We show that hypoxia, through hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), can induce an hESC-like transcriptional program, including the induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) inducers, OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, KLF4, cMYC, and microRNA-302 in 11 cancer cell lines (from prostate, brain, kidney, cervix, lung, colon, liver, and breast tumors). Furthermore, nondegradable forms of HIFα, combined with the traditional iPSC inducers, are highly efficient in generating A549 iPSC-like colonies that have high tumorigenic capacity. To test potential correlation between iPSC inducers and HIF expression in primary tumors, we analyzed primary prostate tumors and found a significant correlation between NANOG-, OCT4-, and HIF1α-positive regions. Furthermore, NANOG and OCT4 expressions positively correlated with increased prostate tumor Gleason score. In primary glioma-derived CD133 negative cells, hypoxia was able to induce neurospheres and hESC markers. Together, these findings suggest that HIF targets may act as key inducers of a dynamic state of stemness in pathologic conditions.
©2011 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Mohyeldin A, Garzon-Muvdi T, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:150–61. - PubMed
-
- Pouyssegur J, Dayan F, Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. 2006;441:437–43. - PubMed
-
- Mabjeesh NJ, Amir S. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in human tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22:559–72. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:105–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS054276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01GM081619-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA112958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083867/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM083867-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM081619/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS054276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116659/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097372/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA116659/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K02 NS047409/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS047409/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

