The diagnostic sensitivity of dengue rapid test assays is significantly enhanced by using a combined antigen and antibody testing approach
- PMID: 21713023
- PMCID: PMC3119643
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001199
The diagnostic sensitivity of dengue rapid test assays is significantly enhanced by using a combined antigen and antibody testing approach
Abstract
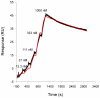
Background: Serological tests for IgM and IgG are routinely used in clinical laboratories for the rapid diagnosis of dengue and can differentiate between primary and secondary infections. Dengue virus non-structural protein 1 (NS1) has been identified as an early marker for acute dengue, and is typically present between days 1-9 post-onset of illness but following seroconversion it can be difficult to detect in serum.
Aims: To evaluate the performance of a newly developed Panbio® Dengue Early Rapid test for NS1 and determine if it can improve diagnostic sensitivity when used in combination with a commercial IgM/IgG rapid test.
Methodology: The clinical performance of the Dengue Early Rapid was evaluated in a retrospective study in Vietnam with 198 acute laboratory-confirmed positive and 100 negative samples. The performance of the Dengue Early Rapid in combination with the IgM/IgG Rapid test was also evaluated in Malaysia with 263 laboratory-confirmed positive and 30 negative samples.
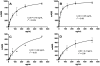
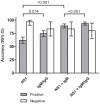
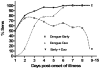
Key results: In Vietnam the sensitivity and specificity of the test was 69.2% (95% CI: 62.8% to 75.6%) and 96% (95% CI: 92.2% to 99.8) respectively. In Malaysia the performance was similar with 68.9% sensitivity (95% CI: 61.8% to 76.1%) and 96.7% specificity (95% CI: 82.8% to 99.9%) compared to RT-PCR. Importantly, when the Dengue Early Rapid test was used in combination with the IgM/IgG test the sensitivity increased to 93.0%. When the two tests were compared at each day post-onset of illness there was clear differentiation between the antigen and antibody markers.
Conclusions: This study highlights that using dengue NS1 antigen detection in combination with anti-glycoprotein E IgM and IgG serology can significantly increase the sensitivity of acute dengue diagnosis and extends the possible window of detection to include very early acute samples and enhances the clinical utility of rapid immunochromatographic testing for dengue.
Conflict of interest statement
SRF, MGS, MM, CM, C-YH and AV are employed by Alere, Australia. MAC was awarded an ARC Linkage Grant with Alere, Australia.
Figures
References
-
- Kyle JL, Harris E. Global Spread and Persistence of Dengue. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2008;62:71–92. - PubMed
-
- Teles FRR, Prazeres DMF, Lima-Filho JL. Trends in dengue diagnosis. Reviews in Medical Virology. 2005;15:287–302. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Strengthening Implementation of the Global Strategy for Dengue Fever/Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever Prevention and Control 2000.
-
- Mairuhu ATA, Wagenaar J, Brandjes DPM, Gorp ECM. Dengue: an arthropod-borne disease of global importance. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 2004;23:425. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever: Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

