Blood pressure reduction combining baroreflex restoration for stroke prevention in hypertension in rats
- PMID: 21713105
- PMCID: PMC3112284
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2010.00006
Blood pressure reduction combining baroreflex restoration for stroke prevention in hypertension in rats
Abstract
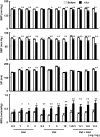
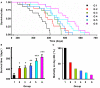
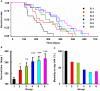
Blood pressure reduction is an important and effective strategy in stroke prevention in hypertensives. Recently, we found that baroreflex restoration was also crucial in stroke prevention. The present work was designed to test the hypothesis that a combination of blood pressure reduction and baroreflex restoration may be a new strategy for stroke prevention. In Experiment 1, the effects of ketanserin (0.3, 1, 3, 10 mg/kg), amlodipine (0.3, 1, 2, 3 mg/kg) and their combination (1 + 0.3, 1 + 1, 1 + 2, 1 + 3 mg/kg) on blood pressure and baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR-SP) were determined under conscious state. It was found that both amlodipine and ketanserin decreased blood pressure dose-dependently. Ketanserin enfanced BRS from a very small dose but amlodipine enfanced BRS only at largest dose used. At the dose of 1 + 2 mg/kg (ketanserin + amlodipine), the combination possessed the largest synergism on blood pressure reduction. In Experiments 2 and 3, SHR-SP and two-kidney, two-clip (2K2C) renovascular hypertensive rats received life-long treatments with ketanserin (1 mg/kg) and amlodipine (2 mg/kg) or their combination (0.5 + 1, 1 + 2, 2 + 4 mg/kg). The survival time was recorded and the brain lesion was examined. It was found that all kinds of treatments prolonged the survival time of SHR-SP and 2K2C rats. The combination possessed a significantly better effect on stroke prevention than mono-therapies. In conclusion, combination of blood pressure reduction and baroreflex restoration may be a new strategy for the prevention of stroke in hypertension.
Keywords: arterial baroreflex; hypertension; prevention; stroke; stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats; two-clip renovascular hypertensive rats; two-kidney.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arterial baroreflex: a novel target for preventing stroke in rat hypertension.Stroke. 2007 Jun;38(6):1916-23. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.106.480061. Epub 2007 Apr 19. Stroke. 2007. PMID: 17446420
-
Effects of combination therapy with atenolol and amlodipine on blood pressure control and stroke prevention in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Nov;28(11):1755-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00630.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17959026
-
Restoration of baroreflex function by ketanserin is not blood pressure dependent in conscious freely moving rats.J Hypertens. 2004 Jun;22(6):1165-72. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200406000-00018. J Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15167452
-
Synergism of irbesartan and amlodipine on hemodynamic amelioration and organ protection in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Sep;32(9):1109-15. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.88. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21804575 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial baroreflex function in conscious rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002 Aug;23(8):673-9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002. PMID: 12147187 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin receptor and tumor necrosis factor-α activation contributes to glucose intolerance independent of systolic blood pressure in obese rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):F1081-F1090. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00156.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29993275 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combination therapy with levamlodipine and bisoprolol on stroke in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013 Mar;19(3):178-82. doi: 10.1111/cns.12057. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013. PMID: 23441690 Free PMC article.
-
Allisartan isoproxil reduces mortality of stroke-prone rats and protects against cerebrovascular, cardiac, and aortic damage.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Jun;42(6):871-884. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00684-7. Epub 2021 May 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 34002042 Free PMC article.
-
Risperidone enhances the vulnerability to stroke in hypertensive rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Apr;18(4):343-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00302.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22486847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daneshtalab N., Smeda J. S. (2010). Alterations in the modulation of cerebrovascular tone and blood flow by nitric oxide synthases in SHRsp with stroke. Cardiovasc. Res. 86, 160–168 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

