Acute murine H5N1 influenza A encephalitis
- PMID: 21714828
- PMCID: PMC3204170
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00514.x
Acute murine H5N1 influenza A encephalitis
Abstract
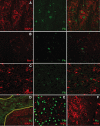
Avian influenza A virus H5N1 has the proven capacity to infect humans through cross-species transmission, but to date, efficient human-to-human transmission is limited. In natural avian hosts, animal models and sporadic human outbreaks, H5N1 infection has been associated with neurological disease. We infected BALB/c mice intranasally with H5N1 influenza A/Viet Nam/1203/2004 to study the immune response during acute encephalitis. Using immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization, we compared the time course of viral infection with activation of immunity. By 5 days postinfection (DPI), mice had lost substantial body weight and required sacrifice by 7 DPI. H5N1 influenza was detected in the lung as early as 1 DPI, whereas infected neurons were not observed until 4 DPI. H5N1 infection of BALB/c mice developed into severe acute panencephalitis. Infected neurons lacked evidence of a perineuronal net and exhibited signs of apoptosis. Whereas lung influenza infection was associated with an early type I interferon (IFN) response followed by a reduction in viral burden concordant with appearance of IFN-γ, the central nervous system environment exhibited a blunted type I IFN response.
© 2011 The Authors. Brain Pathology © 2011 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures




References
-
- Adams I, Brauer K, Arelin C, Hartig W, Fine A, Mader M et al (2001) Perineuronal nets in the rhesus monkey and human basal forebrain including basal ganglia. Neuroscience 108:285–298. - PubMed
-
- Aronsson F, Karlsson H, Ljunggren HG, Kristensson K (2001) Persistence of the influenza A/WSN/33 virus RNA at midbrain levels of immunodefective mice. J Neurovirol 7:117–124. - PubMed
-
- Aronsson F, Lannebo C, Paucar M, Brask J, Kristensson K, Karlsson H (2002) Persistence of viral RNA in the brain of offspring to mice infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus during pregnancy. J Neurovirol 8:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Belichenko PV, Miklossy J, Celio MR (1997) HIV‐I induced destruction of neocortical extracellular matrix components in AIDS victims. Neurobiol Dis 4:301–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

