The ratio of CRP to prealbumin levels predict mortality in patients with hospital-acquired acute kidney injury
- PMID: 21714897
- PMCID: PMC3142490
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-12-30
The ratio of CRP to prealbumin levels predict mortality in patients with hospital-acquired acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Animal and human studies suggest that inflammation and malnutrition are common in acute kidney injury (AKI) patients. However, only a few studies reported CRP, a marker of inflammation, albumin, prealbumin and cholesterol, markers of nutritional status were associated with the prognosis of AKI patients. No study examined whether the combination of inflammatory and nutritional markers could predict the mortality of AKI patients.
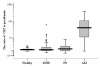
Methods: 155 patients with hospital-acquired AKI were recruited to this prospective cohort study according to RIFLE (Risk, Injury, Failure, Lost or End Stage Kidney) criteria. C-reactive protein (CRP), and the nutritional markers (albumin, prealbumin and cholesterol) measured at nephrology consultation were analyzed in relation to all cause mortality of these patients. In addition, CRP and prealbumin were also measured in healthy controls (n = 45), maintenance hemodialysis (n = 70) and peritoneal dialysis patients (n = 50) and then compared with AKI patients.
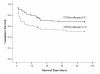
Results: Compared with healthy controls and end-stage renal disease patients on maintenance hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, patients with AKI had significantly higher levels of CRP/prealbumin (p < 0.001). Higher level of serum CRP and lower levels of albumin, prealbumin and cholesterol were found to be significant in the patients with AKI who died within 28 days than those who survived >28 days. Similarly, the combined factors including the ratio of CRP to albumin (CRP/albumin), CRP/prealbumin and CRP/cholesterol were also significantly higher in the former group (p < 0.001 for all). Multivariate analysis (Cox regression) revealed that CRP/prealbumin was independently associated with mortality after adjustment for age, gender, sepsis and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA, p = 0.027) while the others (CRP, albumin, prealbumin, cholesterol, CRP/albumin and CRP/cholesterol) became non-significantly associated. The hazard ratio was 1.00 (reference), 1.85, 2.25 and 3.89 for CRP/prealbumin increasing according to quartiles (p = 0.01 for the trend).
Conclusions: Inflammation and malnutrition were common in patients with AKI. Higher level of the ratio of CRP to prealbumin was associated with mortality of AKI patients independent of the severity of illness and it may be a valuable addition to SOFA score to independent of the severity of illness and it may be a valuable addition to SOFA score to predict the prognosis of AKI patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of prealbumin levels on mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: an observational cohort study.J Ren Nutr. 2008 May;18(3):262-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2007.11.003. J Ren Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18410882
-
Serum prealbumin and its changes over time are associated with mortality in acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 1;7:41493. doi: 10.1038/srep41493. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28145481 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation as a predictor of acute kidney injury and mediator of higher mortality after acute kidney injury in non-cardiac surgery.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 30;9(1):20260. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56615-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31889082 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis of observational clinical studies.Intensive Care Med. 2010 Oct;36(10):1657-1665. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1928-z. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20517593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional Laboratory Markers in Malnutrition.J Clin Med. 2019 May 31;8(6):775. doi: 10.3390/jcm8060775. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31159248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The predictive value of C-reactive protein to albümin ratio for ascending aort progression in patients with ascending aortic diameter of 40-50 mm.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 Oct 4;17(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-02003-5. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36195877 Free PMC article.
-
The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients.J Clin Med. 2018 Oct 8;7(10):333. doi: 10.3390/jcm7100333. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30297655 Free PMC article.
-
The value of serum prealbumin in the diagnosis and therapeutic response of tuberculosis: a retrospective study.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e79940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079940. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260323 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of autophagy is associated with severe ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in overexpressing C-reactive protein mice.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 8;12(9):e0181848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181848. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28886014 Free PMC article.
-
Intake of trans fat and all-cause mortality in the Reasons for Geographical and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) cohort.Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 May;97(5):1121-8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.049064. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23553155 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

