inGAP-sv: a novel scheme to identify and visualize structural variation from paired end mapping data
- PMID: 21715388
- PMCID: PMC3125812
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr506
inGAP-sv: a novel scheme to identify and visualize structural variation from paired end mapping data
Abstract
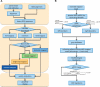
Mining genetic variation from personal genomes is a crucial step towards investigating the relationship between genotype and phenotype. However, compared to the detection of SNPs and small indels, characterizing large and particularly complex structural variation is much more difficult and less intuitive. In this article, we present a new scheme (inGAP-sv) to detect and visualize structural variation from paired-end mapping data. Under this scheme, abnormally mapped read pairs are clustered based on the location of a gap signature. Several important features, including local depth of coverage, mapping quality and associated tandem repeat, are used to evaluate the quality of predicted structural variation. Compared with other approaches, it can detect many more large insertions and complex variants with lower false discovery rate. Moreover, inGAP-sv, written in Java programming language, provides a user-friendly interface and can be performed in multiple operating systems. It can be freely accessed at http://ingap.sourceforge.net/.
Figures
References
-
- Feuk L, Carson AR, Scherer SW. Structural variation in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:85–97. - PubMed
-
- Sharp AJ, Cheng Z, Eichler EE. Structural variation of the human genome. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2006;7:407–442. - PubMed
-
- Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Structural variation in the human genome and its role in disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010;61:437–455. - PubMed
-
- Tuzun E, Sharp AJ, Bailey JA, Kaul R, Morrison VA, Pertz LM, Haugen E, Hayden H, Albertson D, Pinkel D, et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:727–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

