Mammalian orthoreovirus escape from host translational shutoff correlates with stress granule disruption and is independent of eIF2alpha phosphorylation and PKR
- PMID: 21715487
- PMCID: PMC3165827
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01831-10
Mammalian orthoreovirus escape from host translational shutoff correlates with stress granule disruption and is independent of eIF2alpha phosphorylation and PKR
Abstract
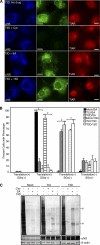
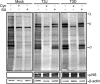
In response to mammalian orthoreovirus (MRV) infection, cells initiate a stress response that includes eIF2α phosphorylation and protein synthesis inhibition. We have previously shown that early in infection, MRV activation of eIF2α phosphorylation results in the formation of cellular stress granules (SGs). In this work, we show that as infection proceeds, MRV disrupts SGs despite sustained levels of phosphorylated eIF2α and, further, interferes with the induction of SGs by other stress inducers. MRV interference with SG formation occurs downstream of eIF2α phosphorylation, suggesting the virus uncouples the cellular stress signaling machinery from SG formation. We additionally examined mRNA translation in the presence of SGs induced by eIF2α phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. We found that irrespective of eIF2α phosphorylation status, the presence of SGs in cells correlated with inhibition of viral and cellular translation. In contrast, MRV disruption of SGs correlated with the release of viral mRNAs from translational inhibition, even in the presence of phosphorylated eIF2α. Viral mRNAs were also translated in the presence of phosphorylated eIF2α in PKR(-/-) cells. These results suggest that MRV escape from host cell translational shutoff correlates with virus-induced SG disruption and occurs in the presence of phosphorylated eIF2α in a PKR-independent manner.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mammalian orthoreovirus particles induce and are recruited into stress granules at early times postinfection.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):11090-101. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01239-09. Epub 2009 Aug 26. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19710141 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Orthoreovirus Factories Modulate Stress Granule Protein Localization by Interaction with G3BP1.J Virol. 2017 Oct 13;91(21):e01298-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01298-17. Print 2017 Nov 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28794026 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Norovirus Infection Arrests Host Cell Translation Uncoupled from the Stress Granule-PKR-eIF2α Axis.mBio. 2019 Jun 18;10(3):e00960-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00960-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31213553 Free PMC article.
-
The role of host eIF2α in viral infection.Virol J. 2020 Jul 23;17(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01362-6. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32703221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reovirus and the Host Integrated Stress Response: On the Frontlines of the Battle to Survive.Viruses. 2021 Jan 28;13(2):200. doi: 10.3390/v13020200. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33525628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of stress granules and P-bodies during RNA virus infection.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 May-Jun;4(3):317-31. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1162. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23554219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational Control in Virus-Infected Cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):a033001. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033001. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 29891561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoplasmic RNA Granules and Viral Infection.Annu Rev Virol. 2014 Nov;1(1):147-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-031413-085505. Annu Rev Virol. 2014. PMID: 26958719 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Type 1 Interferon Responses Are Critical for Control of Systemic Reovirus Dissemination.J Virol. 2021 Jan 28;95(4):e02167-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02167-20. Print 2021 Jan 28. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33208448 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A virus PB1-F2 protein expression is regulated in a strain-specific manner by sequences located downstream of the PB1-F2 initiation codon.J Virol. 2013 Oct;87(19):10687-99. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01520-13. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23885074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brendler T., Godefroy-Colburn T., Yu S., Thach R. E. 1981. The role of mRNA competition in regulating translation. III. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo results. J. Biol. Chem. 256:11755–11761 - PubMed
-
- Dang Y., et al. 2006. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α-independent pathway of stress granule induction by the natural product pateamine A. J. Biol. Chem. 281:32870–32878 - PubMed
-
- Detjen B. M., Walden W. E., Thach R. E. 1982. Translational specificity in reovirus-infected mouse fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 257:9855–9860 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

