Benefits of Renin-Angiotensin blockade on retinopathy in type 1 diabetes vary with glycemic control
- PMID: 21715517
- PMCID: PMC3142059
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-0476
Benefits of Renin-Angiotensin blockade on retinopathy in type 1 diabetes vary with glycemic control
Abstract
Objective: Optimal glycemic control slows diabetic retinopathy (DR) development and progression and is the standard of care for type 1 diabetes. However, these glycemic goals are difficult to achieve and sustain in clinical practice. The Renin Angiotensin System Study (RASS) showed that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade can slow DR progression. In the current study, we evaluate whether glycemic control influenced the benefit of RAS blockade on DR progression in type 1 diabetic patients.
Research design and methods: We used RASS data to analyze the relationships between two-steps or more DR progression and baseline glycemic levels in 223 normotensive, normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients randomized to receive 5 years of enalapril or losartan compared with placebo.
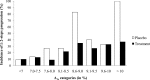
Results: A total of 147 of 223 patients (65.9%) had DR at baseline (47 of 74 patients [63.5%] in placebo and 100 of 149 patients [67.1%] in the combined treatment groups [P = 0.67]). Patients with two-steps or more DR progression had higher baseline A1C than those without progression (9.4 vs. 8.2%, P < 0.001). There was no beneficial effect of RAS blockade (P = 0.92) in patients with baseline A1C ≤7.5%. In contrast, 30 of 112 (27%) patients on the active treatment arms with A1C >7.5% had two-steps or more DR progression compared with 26 of 56 patients (46%) in the placebo group (P = 0.03).
Conclusions: RAS blockade reduces DR progression in normotensive, normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients with A1C >7.5%. Whether this therapy could benefit patients with A1C ≤7.5% will require long-term studies of much larger cohorts.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00143949.
Figures
References
-
- Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, et al. ; American Diabetes Association. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27(Suppl. 1):S84–S87 - PubMed
-
- Saaddine JB, Honeycutt AA, Narayan KM, Zhang X, Klein R, Boyle JP. Projection of diabetic retinopathy and other major eye diseases among people with diabetes mellitus: United States, 2005-2050. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126:1740–1747 - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–853 - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed