Human apoE isoforms differentially regulate brain amyloid-β peptide clearance
- PMID: 21715678
- PMCID: PMC3192364
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002156
Human apoE isoforms differentially regulate brain amyloid-β peptide clearance
Abstract
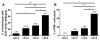
The apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset, sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD). The APOE ε4 allele markedly increases AD risk and decreases age of onset, likely through its strong effect on the accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide. In contrast, the APOE ε2 allele appears to decrease AD risk. Most rare, early-onset forms of familial AD are caused by autosomal dominant mutations that often lead to overproduction of Aβ(42) peptide. However, the mechanism by which APOE alleles differentially modulate Aβ accumulation in sporadic, late-onset AD is less clear. In a cohort of cognitively normal individuals, we report that reliable molecular and neuroimaging biomarkers of cerebral Aβ deposition vary in an apoE isoform-dependent manner. We hypothesized that human apoE isoforms differentially affect Aβ clearance or synthesis in vivo, resulting in an apoE isoform-dependent pattern of Aβ accumulation later in life. Performing in vivo microdialysis in a mouse model of Aβ-amyloidosis expressing human apoE isoforms (PDAPP/TRE), we find that the concentration and clearance of soluble Aβ in the brain interstitial fluid depends on the isoform of apoE expressed. This pattern parallels the extent of Aβ deposition observed in aged PDAPP/TRE mice. ApoE isoform-dependent differences in soluble Aβ metabolism are observed not only in aged but also in young PDAPP/TRE mice well before the onset of Aβ deposition in amyloid plaques in the brain. Additionally, amyloidogenic processing of amyloid precursor protein and Aβ synthesis, as assessed by in vivo stable isotopic labeling kinetics, do not vary according to apoE isoform in young PDAPP/TRE mice. Our results suggest that APOE alleles contribute to AD risk by differentially regulating clearance of Aβ from the brain, suggesting that Aβ clearance pathways may be useful therapeutic targets for AD prevention.
Figures





References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, George-Hyslop PH, Pericak-Vance MA, Joo SH, Rosi BL, Gusella JF, Crapper-MacLachlan DR, Alberts MJ, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Risch NJ, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Jr., Rimmler JB, Locke PA, Conneally PM, Schmader KE, et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1994;7:180–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30NS069329-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG13956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG05681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG034004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG034004/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS069329/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23-AG03094601/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS069329/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG03991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG030946/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG035083/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

