Recessive axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to compound heterozygous mitofusin 2 mutations
- PMID: 21715711
- PMCID: PMC3140074
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182242d4d
Recessive axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to compound heterozygous mitofusin 2 mutations
Abstract
Objective: Mutations in mitofusin 2 (MFN2) are the most common cause of axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT2). Over 50 mutations have been reported, mainly causing autosomal dominant disease, though families with homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations have been described. We present 3 families with early-onset CMT2 associated with compound heterozygous MFN2 mutations. Transcriptional analysis was performed to investigate the effects of the mutations.
Methods: Patients were examined clinically and electrophysiologically; parents were also examined where available. Genetic investigations included MFN2 DNA sequencing and dosage analysis by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. MFN2 mRNA transcripts from blood lymphocytes were analyzed in 2 families.
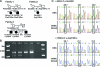
Results: Compound heterozygosity for MFN2 mutations was associated with early-onset CMT2 of varying severity between pedigrees. Parents, where examined, were unaffected and were heterozygous for the expected mutations. Four novel mutations were detected (one missense, one nonsense, an intragenic deletion of exons 7 + 8, and a 3-base pair deletion), as well as 2 previously reported missense mutations. Transcriptional analysis demonstrated aberrant splicing of the exonic deletion and indicated nonsense-mediated decay of mutant alleles with premature truncating mutations.
Conclusions: Our findings confirm that MFN2 mutations can cause early-onset CMT2 with apparent recessive inheritance. Novel genetic findings include an intragenic MFN2 deletion and nonsense-mediated decay. Carrier parents were asymptomatic, suggesting that MFN2 null alleles can be nonpathogenic unless coinherited with another mutation.
Figures
References
-
- Züchner S, Mersiyanova IV, Muglia M, et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 2A. Nat Genet 2004;36:449–451 - PubMed
-
- Verhoeven K, Claeys KG, Züchner S, et al. MFN2 mutation distribution and genotype/phenotype correlation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2. Brain 2006;129:2093–2102 - PubMed
-
- Chung KW, Kim SB, Park KD, et al. Early onset severe and late-onset mild Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with mitofusin 2 (MFN2) mutations. Brain 2006;129:2103–2118 - PubMed
-
- Cartoni R, Martinou JC. Role of mitofusin 2 mutations in the physiopathology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A. Exp Neurol 2009;218:268–273 - PubMed
-
- Nicholson GA, Magdelaine C, Zhu D, et al. Severe early-onset axonal neuropathy with homozygous and compound heterozygous MFN2 mutations. Neurology 2008;70:1678–1681 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
