Effects of encapsulated propolis on blood glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
- PMID: 21716678
- PMCID: PMC3118452
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/981896
Effects of encapsulated propolis on blood glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
Abstract
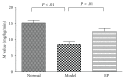
The present study investigates the encapsulated propolis on blood glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats. The animal characteristics and biological assays of body weight, fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting serum insulin (FINS), insulin act index (IAI), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were measured and euglycemic hyperinsulinemic glucose clamp technique were used to determine these effects. Our findings show that oral administration of encapsulated propolis can significantly inhibit the increasing of FBG and TG in T2DM rats and can improve IAI and M value in euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp experiment. There was no significant effects on body weight, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C in T2DM rats treated with encapsulated propolis. In conclusion, the results indicate that encapsulated propolis can control blood glucose, modulate lipid metabolism, and improve the insulin sensitivity in T2DM rats.
Figures

References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(9):1414–1431. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health Peoples Republic of China MoSaToPRoC, National Bureau of Statistics of China. An Investigation on Health and Nutrition Status of Chinese Resident. Beijing, China: People's Health Publishing House; 2005.
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Davì G, Santilli F, Patrono C. Nutraceuticals in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Cardiovascular Therapeutics. 2010;28(4):216–226. - PubMed
-
- Jermendy G. Can type 2 diabetes mellitus be considered preventable? Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005;68(supplement 1):S73–S81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

