Kappa-opioid receptor activation during reperfusion limits myocardial infarction via ERK1/2 activation in isolated rat hearts
- PMID: 21716908
- PMCID: PMC3110294
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.60.5.351
Kappa-opioid receptor activation during reperfusion limits myocardial infarction via ERK1/2 activation in isolated rat hearts
Abstract
Background: We investigated whether p42/p44 extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) and/or phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI3K)-Akt play a crucial role in cardioprotection by κ-opioid receptor (KOP) activation.
Methods: Langendorff perfused rat hearts were subjected to 30 min of regional ischemia and 2 h of reperfusion. Antagonists of ERK1/2 and PI3K were perfused in hearts treated with the KOP agonist U50488H (U50). Infarct size was measured after 2 h of reperfusion. The phosphorylation states of ERK1/2 and Akt by Western immunoblots were determined. Drugs were perfused for a period of 5 min before and 30 min after reperfusion.
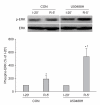
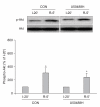
Results: Inhibition of ERK1/2 (26.8 ± 2.9%, P < 0.05 vs. U50) but not PI3K (15.5 ± 1.1%, P > 0.05 vs. U50) completely abrogated the anti-infarct effect of U50488H. Western blot analysis revealed a significant increase in ERK1/2 but not Akt phsophorylation in U50488H-treated hearts as compared to control hearts when measured immediately after reperfusion.
Conclusions: KOP activation effectively reduces myocardial infarction. The anti-infarct effect of U50488H is mediated by the ERK1/2, but not the PI3K-Akt pathway.
Keywords: Coronary occlusion; Heart; Myocardial function; Opioid receptors; Reperfusion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
δ-Opioid Receptor as a Molecular Target for Increasing Cardiac Resistance to Reperfusion in Drug Development.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 3;11(7):1887. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071887. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotection by kappa-opioid receptor agonist U50488H is mediated by opioidergic regulation but not by calcium current modulation.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010 Feb;58(2):162-8. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.2.162. Epub 2010 Feb 28. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010. PMID: 20498795 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of kappa-opioid receptors at reperfusion affords cardioprotection in both rat and mouse hearts.Basic Res Cardiol. 2008 Sep;103(5):454-63. doi: 10.1007/s00395-008-0726-z. Epub 2008 May 23. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18500486
-
Ischemic postconditioning protects remodeled myocardium via the PI3K-PKB/Akt reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Oct 1;72(1):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.06.027. Epub 2006 Jul 6. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16901477
-
Phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-protein kinase B and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 mediate reoxygenation-induced cardioprotection during hypoxia.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010 Mar;235(3):401-10. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2009.009153. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2010. PMID: 20404059
Cited by
-
Postconditioning signalling in the heart: mechanisms and translatability.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;172(8):1933-46. doi: 10.1111/bph.12976. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25303373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Remyelination through a Novel Opioid-Receptor Pathway.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 23;36(47):11831-11833. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2859-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27881770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Morphine and remifentanil-induced cardioprotection: its experimental and clinical outcomes.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2011 Nov;61(5):358-66. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2011.61.5.358. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2011. PMID: 22148082 Free PMC article.
-
δ-Opioid Receptor as a Molecular Target for Increasing Cardiac Resistance to Reperfusion in Drug Development.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 3;11(7):1887. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071887. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynorphins in Development and Disease: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Mol Med. 2020;20(4):259-274. doi: 10.2174/1566524019666191028122559. Curr Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31746302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zaugg M, Lucchinetti E, Uecker M, Pasch T, Schaub MC. Anaesthetics and cardiac preconditioning. Part I. Signalling and cytoprotective mechanisms. Br J Anaesth. 2003;91:551–565. - PubMed
-
- Gross ER, Hsu AK, Gross GJ. Opioid-induced cardioprotection occurs via glycogen synthase kinase beta inhibition during reperfusion in intact rat hearts. Circ Res. 2004;94:960–966. - PubMed
-
- Okubo S, Tanabe Y, Takeda K, Kitayama M, Kanemitsu S, Kukreja RC, et al. Ischemic preconditioning and morphine attenuate myocardial apoptosis and infarction after ischemia-reperfusion in rabbit: role of delta-opioid receptor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287:H1786–H1791. - PubMed
-
- Xia Q, Zhang WM, Shen YL, Wong TM. Decreased affinity for K-receptor binding during reperfusion following ischaemic preconditioning in the rat heart. Life Sci. 1996;58:1307–1313. - PubMed
-
- Chang WL, Lee SS, Su MJ. Attenuation of post-ischemia reperfusion injury by thaliporphine and morphine in rat hearts. J Biomed Sci. 2005;12:611–619. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

