Exercise intensity and oxygen uptake kinetics in African-American and Caucasian women
- PMID: 21717119
- PMCID: PMC3329968
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-011-2054-5
Exercise intensity and oxygen uptake kinetics in African-American and Caucasian women
Abstract
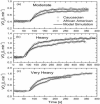
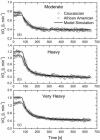
The effect of exercise intensity on the on- and off-transient kinetics of oxygen uptake (VO(2)) was investigated in African American (AA) and Caucasian (C) women. African American (n = 7) and Caucasian (n = 6) women of similar age, body mass index and weight, performed an incremental test and bouts of square-wave exercise at moderate, heavy and very heavy intensities on a cycle ergometer. Gas exchange threshold (LT(GE)) was lower in AA (13.6 ± 2.3 mL kg(-1) min(-1)) than C (18.6 ± 5.6 mL kg(-1) min(-1)). The dynamic exercise and recovery VO(2) responses were characterized by mathematical models. There were no significant differences in (1) peak oxygen uptake (VO(2peak)) between AA (28.5 ± 5 mL kg(-1) min(-1)) and C (31.1 ± 6.6 mL kg(-1) min(-1)) and (2) VO(2) kinetics at any exercise intensity. At moderate exercise, the on- and off- VO(2) kinetics was described by a monoexponential function with similar time constants τ (1,on) (39.4 ± 12.5; 38.8 ± 15 s) and τ (1,off) (52.7 ± 10.1; 40.7 ± 4.4 s) for AA and C, respectively. At heavy and very heavy exercise, the VO(2) kinetics was described by a double-exponential function. The parameter values for heavy and very heavy exercise in the AA group were, respectively: τ (1,on) (47.0 ± 10.8; 44.3 ± 10 s), τ (2,on) (289 ± 63; 219 ± 90 s), τ (1,off) (45.9 ± 6.2; 50.7 ± 10 s), τ (2,off) (259 ± 120; 243 ± 93 s) while in the C group were, respectively: τ (1,on) (41 ± 12; 43.2 ± 15 s); τ (2, on) (277 ± 81; 215 ± 36 s), τ (1,off) (40.2 ± 3.4; 42.3 ± 7.2 s), τ (2,off) (215 ± 133; 228 ± 64 s). The on- and off-transients were symmetrical with respect to model order and dependent on exercise intensity regardless of race. Despite similar VO(2) kinetics, LT(GE) and gain of the VO(2) on-kinetics at moderate intensity were lower in AA than C. However, generalization to the African American and Caucasian populations is constrained by the small subject numbers.
Figures
References
-
- Ama PFM, Simoneau JA, Boulay MR, Serresse O, Thěriault G, Bouchard C. Skeletal muscle characteristics in sedentary Black and Caucasian males. J Appl Physiol. 1986;61(5):758–1761. - PubMed
-
- Barstow TJ, Mole PA. Linear and nonlinear characteristics of oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1991;71(6):2099–2106. - PubMed
-
- Barstow TJ, Jones AM, Nguyen PH, Casaburi R. Influence of muscle fiber type and pedal frequency on oxygen uptake kinetics of heavy exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81(4):1642–1650. - PubMed
-
- Bauer TA, Brass EP, Nehler M, Barstow TJ, Hiatt WR. Pulmonary VO2 dynamics during treadmill and arm exercise in peripheral arterial disease. J Appl Physiol. 2004;97:627–634. - PubMed
-
- Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol. 1986;60:2020–2027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

