Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein reduces intracellular accumulation of beta amyloid: investigation of P-glycoprotein as a novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21718295
- PMCID: PMC3163078
- DOI: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01309.x
Up-regulation of P-glycoprotein reduces intracellular accumulation of beta amyloid: investigation of P-glycoprotein as a novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objectives: Several studies have suggested the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) to play a role in the etiology of Alzheimer's disease through the clearance of amyloid beta (Aβ) from the brain. In this study, we aimed to investigate the possibility of P-gp as a potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease by examining the impact of P-gp up-regulation on the clearance of Aβ, a neuropathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease.
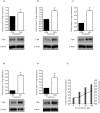
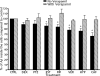
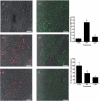
Methods: Uptake studies for ¹²⁵I-radiolabelled Aβ₁₋₄₀, and fluorescent immunostaining technique for P-gp and fluorescent imaging of Aβ₁₋₄₀ were carried out in LS-180 cells following treatment with drugs known to induce P-gp expression.
Key findings: Approximately 10-35% decrease in ¹²⁵I-Aβ₁₋₄₀ intracellular accumulation was observed in cells treated with rifampicin, dexamethasone, caffeine, verapamil, hyperforin, β-estradiol and pentylenetetrazole compared with control. Also, fluorescent micrographs showed an inverse relationship between levels of P-gp expression and 5-carboxyfluorescein labelled Aβ (FAM-Aβ₁₋₄₀) intracellular accumulation. Quantitative analysis of the micrographs revealed that the results were consistent with those of the uptake studies using ¹²⁵I-Aβ₁₋₄₀.
Conclusions: The investigated drugs were able to improve the efflux of Aβ₁₋₄₀ from the cells via P-gp up-regulation compared with control. Our results elucidate the importance of targeting Aβ clearance via P-gp up-regulation, which will be effective in slowing or halting the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
© 2011 The Authors. JPP © 2011 Royal Pharmaceutical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Maslow K. 2010 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2010;6:158–194. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741–766. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic BV, Frangione B. Transport-clearance hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease and potential therapeutic implications. In: Saido TC, editor. Aβ Metabolism in Alzheimer's Disease. Landes Bioscience; Georgetown, TX: 2003. pp. 114–122.
-
- Vogelgesang S, et al. Deposition of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid is inversely correlated with P-glycoprotein expression in the brains of elderly non-demented humans. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12:535–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

