Consequences of splice variation on Secretin family G protein-coupled receptor function
- PMID: 21718310
- PMCID: PMC3415641
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01571.x
Consequences of splice variation on Secretin family G protein-coupled receptor function
Abstract
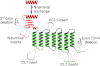
The Secretin family of GPCRs are endocrine peptide hormone receptors that share a common genomic organization and are the subject of a wide variety of alternative splicing. All GPCRs contain a central seven transmembrane domain responsible for transducing signals from the outside of the cell as well as extracellular amino and intracellular carboxyl termini. Members of the Secretin receptor family have a relatively large N-terminus and a variety of lines of evidence support a common mode of ligand binding and a common ligand binding fold. These receptors are best characterized as coupling to intracellular signalling pathways via G(αs) and G(αq) but are also reported to couple to a multitude of other signalling pathways. The intracellular loops are implicated in regulating the interaction between the receptor and heterotrimeric G protein complexes. Alternative splicing of exons encoding both the extracellular N-terminal domain as well as the extracellular loops of some family members has been reported and as expected these splice variants display altered ligand affinity as well as differential activation by endogenous ligands. Various forms of alternative splicing have also been reported to alter intracellular loops 1 and 3 as well as the C-terminus and as one might expect these display differences in signalling bias towards downstream effectors. These diverse pharmacologies require that the physiological role of these splice variants be addressed but should provide unique opportunities for drug design and development.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Albrandt K, Mull E, Brady EM, Herich J, Moore CX, Beaumont K. Molecular cloning of two receptors from rat brain with high affinity for salmon calcitonin. FEBS Lett. 1993;325:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Ardati A, Goetschy V, Gottowick J, Henriot S, Valdenaire O, Deuschle U, et al. Human CRF2 alpha and beta splice variants: pharmacological characterization using radioligand binding and a luciferase gene expression assay. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:441–448. - PubMed
-
- Bazarsuren A, Grauschopf U, Wozny M, Reusch D, Hoffmann E, Schaefer W, et al. In vitro folding, functional characterization, and disulfide pattern of the extracellular domain of human GLP-1 receptor. Biophys Chem. 2002;96:305–318. - PubMed
-
- Bergwitz C, Gardella TJ, Flannery MR, Potts JT, Kronenberg HM, Goldring SR, et al. Full activation of chimeric receptors by hybrids between parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Evidence for a common pattern of ligand-receptor interaction. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:26469–26472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

