Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis
- PMID: 21719792
- PMCID: PMC3137582
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011010062
Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis
Abstract
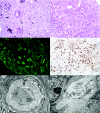
IgG4-related systemic disease is an autoimmune disease that was first recognized in the pancreas but also affects other organs. This disease may manifest as tubulointerstitial nephritis (IgG4-TIN), but its clinicopathologic features in the kidney are not well described. Of the 35 patients with IgG4-TIN whose renal tissue specimens we examined, 27 (77%) had acute or progressive chronic renal failure, 29 (83%) had involvement of other organ systems, and 18 of 23 (78%) had radiographic abnormalities. Elevated total IgG or IgG4 serum levels were present in 79%. All pathologic specimens featured plasma cell-rich TIN, with most showing diffuse, expansile interstitial fibrosis. Immune complexes along the tubular basement membranes were present in 25 of 30 (83%). All specimens had a moderate to marked increase in IgG4+ plasma cells by immunohistochemistry. We used a control group of 175 pathologic specimens with plasma cell-rich interstitial infiltrates that can mimic IgG4-TIN to examine the diagnostic utility of IgG4 immunostaining. Excluding pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis, IgG4 immunohistochemistry had a sensitivity of 100% (95% CI 90-100%) and a specificity of 92% (95% CI 86-95%) for IgG4-TIN. Of the 19 patients with renal failure for whom treatment and follow-up data were available, 17 (89%) responded to prednisone. In summary, because no single test definitively diagnoses IgG4-related systemic disease, we rely on a combination of histologic, immunophenotypic, clinical, radiographic, and laboratory features. When the disease manifests in the kidney, our data support diagnostic criteria that can distinguish IgG4-TIN from other types of TIN.
Copyright © 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology
Figures
References
-
- Deshpande V, Chicano S, Finkelberg D, Selig MK, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge WR, Colvin RB, Lauwers GY: Autoimmune pancreatitis: A systemic immune complex mediated disease. Am J Surg Pathol 30: 1537–1545, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N, Nakajima H: A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol 38: 982–984, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Shrestha B, Sekiguchi H, Colby TV, Graziano P, Aubry MC, Smyrk TC, Feldman AL, Cornell LD, Ryu JH, Chari ST, Dueck AC, Yi ES: Distinctive pulmonary histopathology with increased IgG4-positive plasma cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: Report of 6 and 12 cases with similar histopathology. Am J Surg Pathol 33: 1450–1462, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Kasahara Y, Horita K, Miyayama S, Miura S, Kitagawa S, Nakanuma Y: Inflammatory pseudotumor of the breast in a patient with a high serum IgG4 level: Histologic similarity to sclerosing pancreatitis. Am J Surg Pathol 29: 275–278, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Uehara T, Hamano H, Kawa S, Sano K, Honda T, Ota H: Distinct clinicopathological entity ‘autoimmune pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis’. Pathol Int 55: 405–411, 2005 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

