Angiotensin II activation of mTOR results in tubulointerstitial fibrosis through loss of N-cadherin
- PMID: 21720156
- PMCID: PMC3130895
- DOI: 10.1159/000329327
Angiotensin II activation of mTOR results in tubulointerstitial fibrosis through loss of N-cadherin
Abstract
Background/aims: Angiotensin (Ang) II contributes to tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Recent data highlight mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) signaling in tubulointerstitial fibrosis; however, the mechanisms remain unclear. Thereby, we investigated the role of Ang II on mTOR/S6K1-dependent proximal tubule (PT) injury, remodeling, and fibrosis.
Methods: We utilized young transgenic Ren2 rats (R2-T) and Sprague-Dawley rats (SD-T) treated with the Ang type 1 receptor (AT(1)R) blocker telmisartan (2 mg · kg(-1) · day(-1)) or vehicle (R2-C; SD-C) for 3 weeks to examine PT structure and function.
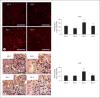
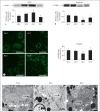
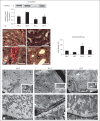
Results: Ren2 rats displayed increased systolic blood pressure, proteinuria and increased PT oxidant stress and remodeling. There were parallel increases in kidney injury molecule-1 and reductions in neprilysin and megalin with associated ultrastructural findings of decreased clathrin-coated pits, endosomes, and vacuoles. Ren2 rats displayed increased Serine(2448) phosphorylation of mTOR and downstream S6K1, in concert with ultrastructural basement membrane thickening, tubulointerstitial fibrosis and loss of the adhesion molecule N-cadherin. Telmisartan treatment attenuated proteinuria as well as the biochemical and tubulointerstitial structural abnormalities seen in the Ren2 rats.
Conclusions: Our observations suggest that Ang II activation of the AT(1)R contributes to PT brush border injury and remodeling, in part, due to enhanced mTOR/S6K1 signaling which promotes tubulointerstitial fibrosis through loss of N-cadherin.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Eddy AA. Progression in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2005;12:353–365. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Iturbe B, García García G. The role of tubulointerstitial inflammation in the progression of chronic renal failure. Nephron Clin Pract. 2010;116:c81–c88. - PubMed
-
- Fujii H, Kono K, Nakai K, Goto S, Komaba H, Hamada Y, Shinohara M, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Fukagawa M. Oxidative and nitrosative stress and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes. Am J Nephrol. 2010;31:342–352. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Kalluri R. Cellular and molecular pathways that lead to progression and regression of renal fibrogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 2005;5:467–474. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR. Metabolic risk factors and renal disease. Kidney Int. 2007;71:719–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

