Real time analysis of β(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated signaling kinetics in human primary airway smooth muscle cells reveals both ligand and dose dependent differences
- PMID: 21722392
- PMCID: PMC3143098
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-89
Real time analysis of β(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated signaling kinetics in human primary airway smooth muscle cells reveals both ligand and dose dependent differences
Abstract
Background: β2-adrenoceptor agonists elicit bronchodilator responses by binding to β2-adrenoceptors on airway smooth muscle (ASM). In vivo, the time between drug administration and clinically relevant bronchodilation varies significantly depending on the agonist used. Our aim was to utilise a fluorescent cyclic AMP reporter probe to study the temporal profile of β2-adrenoceptor-mediated signaling induced by isoproterenol and a range of clinically relevant agonists in human primary ASM (hASM) cells by using a modified Epac protein fused to CFP and a variant of YFP.
Methods: Cells were imaged in real time using a spinning disk confocal system which allowed rapid and direct quantification of emission ratio imaging following direct addition of β2-adrenoceptor agonists (isoproterenol, salbutamol, salmeterol, indacaterol and formoterol) into the extracellular buffer. For pharmacological comparison a radiolabeling assay for whole cell cyclic AMP formation was used.
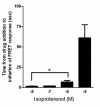
Results: Temporal analysis revealed that in hASM cells the β2-adrenoceptor agonists studied did not vary significantly in the onset of initiation. However, once a response was initiated, significant differences were observed in the rate of this response with indacaterol and isoproterenol inducing a significantly faster response than salmeterol. Contrary to expectation, reducing the concentration of isoproterenol resulted in a significantly faster initiation of response.
Conclusions: We conclude that confocal imaging of the Epac-based probe is a powerful tool to explore β2-adrenoceptor signaling in primary cells. The ability to analyse the kinetics of clinically used β2-adrenoceptor agonists in real time and at a single cell level gives an insight into their possible kinetics once they have reached ASM cells in vivo.
Figures


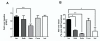


References
-
- Hall IP TA. In: Asthma. 3. Clark TH GS, Lee TH, editor. London: Chapman and Hall; 1992. Beta-agonists; pp. 341–365.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

