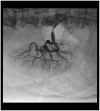
Renal artery stenosis: optimizing diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 21722784
- PMCID: PMC4801483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcad.2011.02.007
Renal artery stenosis: optimizing diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is the most commonly caused by atherosclerosis, with fibromuscular dysplasia being the most frequent among other less common etiologies. A high index of suspicion based on clinical features is essential for diagnosis. Revascularization strategies are currently a topic of discussion and debate. When revascularization is deemed appropriate, atherosclerotic RAS is most often treated with stent placement, whereas patients with fibromuscular dysplasia are usually treated with balloon angioplasty. Ongoing randomized trials should help to better define the optimal management of RAS.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Trinquart L, Mounier-Vehier C, Sapoval M, Gagnon N, Plouin PF. Efficacy of Revascularization For Renal Artery Stenosis Caused by Fibromuscular Dysplasia, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension. 2010;56:525–532. - PubMed
-
- Krijnen P, van Jaarsveld BC, Steyerberg EW, Man in ‘t Veld AJ, Schalekamp MA, Habbema JD. A clinical prediction rule for renal artery stenosis. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Nov 1;129(9):705–11. - PubMed
-
- Krijnen P, Steyerberg EW, Postma CT, Flobbe K, de Leeuw PW, Hunink MG. Validation of a prediction rule for renal artery stenosis. J Hypertens. 2005 Aug;23(8):1583–8. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MG, Pascua JA, Garcia-Ben M, Rojas-Matas CA, Gabay JM, Berrocal DH, Tan WA, Stouffer GA, Montoya M, Fernandez AD, Halac ME, Grinfeld LR. A simple prediction rule for significant renal artery stenosis in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Am Heart J. 2005 Dec;150(6):1204–11. - PubMed
-
- Rigatelli G, Rigatelli G. Assessing the appropriateness and increasing the yield of renal angiography in patients undergoing coronary angiography: a scoring system. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2006 Apr;22(2):135–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical