Ventral tegmental area-basolateral amygdala-nucleus accumbens shell neurocircuitry controls the expression of heroin-conditioned immunomodulation
- PMID: 21722970
- PMCID: PMC3576037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.06.002
Ventral tegmental area-basolateral amygdala-nucleus accumbens shell neurocircuitry controls the expression of heroin-conditioned immunomodulation
Abstract
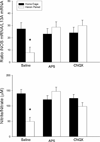
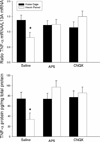
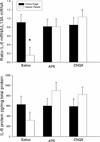
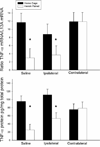
The present investigations sought to determine whether the ventral tegmental area (VTA), basolateral amygdala (BLA), and nucleus accumbens shell (NAC) comprise a circuitry that mediates heroin-induced conditioned immunomodulation. Rats were given conditioning trials in which they received an injection of heroin upon placement into a distinctive environment. Prior to testing, rats received unilateral intra-BLA microinfusion of a D(1) antagonist concomitantly with unilateral intra-NAC shell microinfusion of an NMDA antagonist. Disconnection of the VTA-BLA-NAC circuit impaired the ability of the heroin-paired environment to suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced immune responses, defining for the first time a specific neural circuit involved in conditioned neural-immune interactions.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Region-specific contribution of the ventral tegmental area to heroin-induced conditioned immunomodulation.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 May;38:118-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24462948 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned effects of heroin on proinflammatory mediators require the basolateral amygdala.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Nov;28(9):1867-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06472.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973600 Free PMC article.
-
Inputs from the basolateral amygdala to the nucleus accumbens shell control opiate reward magnitude via differential dopamine D1 or D2 receptor transmission.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Jan;35(2):279-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07943.x. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22236063
-
Cannabinoid reward and aversion effects in the posterior ventral tegmental area are mediated through dissociable opiate receptor subtypes and separate amygdalar and accumbal dopamine receptor substrates.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Aug;234(15):2325-2336. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4669-7. Epub 2017 Jul 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28669034
-
Optogenetic interrogations of the neural circuits underlying addiction.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;23(4):539-45. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23375167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heroin-induced conditioned immunomodulation requires expression of IL-1β in the dorsal hippocampus.Brain Behav Immun. 2013 May;30:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.01.076. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2013. PMID: 23357470 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced volume of the nucleus accumbens in heroin addiction.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015 Dec;265(8):637-45. doi: 10.1007/s00406-014-0564-y. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25467383 Clinical Trial.
-
Acquisition of heroin conditioned immunosuppression requires IL-1 signaling in the dorsal hippocampus.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Aug;56:325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 27072068 Free PMC article.
-
CCR5 mediates HIV-1 Tat-induced neuroinflammation and influences morphine tolerance, dependence, and reward.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Mar;69:124-138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29146238 Free PMC article.
-
Female rats express heroin-induced and -conditioned suppression of peripheral nitric oxide production in response to endotoxin challenge.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Jan;91:315-323. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.10.009. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33039661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backstrom P, Hyytia P. Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2007;192(4):571–580. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AE, Holahan MR, Sadeghian K, Kelley AE. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent plasticity within a distributed corticostriatal network mediates appetitive instrumental learning. Behav Neurosci. 2000;114(1):84–98. - PubMed
-
- Bandaletova T, Brouet I, Bartsch H, Sugimura T, Esumi H, Ohshima H. Immunohistochemical localization of an inducible form of nitric oxide synthase in various organs of rats treated with Propionibacteriumacnes and lipopolysaccharide. Apmis. 1993;101:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Belin D, Everitt BJ. Cocaine seeking habits depend upon dopamine-dependent serial connectivity linking the ventral with the dorsal striatum. Neuron. 2008;57(3):432–441. - PubMed
-
- Benscsics A, Elenkov IJ, Vizi ES. Effect of morphine on lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vivo: involvement of the sympathetic nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 1997;73(1–2):1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

