Innervation patterns of autonomic axons in the human endocrine pancreas
- PMID: 21723503
- PMCID: PMC3135265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.05.008
Innervation patterns of autonomic axons in the human endocrine pancreas
Abstract
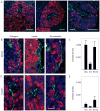
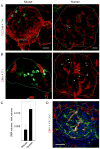
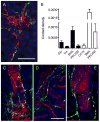
The autonomic nervous system regulates hormone secretion from the endocrine pancreas, the islets of Langerhans, thus impacting glucose metabolism. The parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves innervate the pancreatic islet, but the precise innervation patterns are unknown, particularly in human. Here we demonstrate that the innervation of human islets is different from that of mouse islets and does not conform to existing models of autonomic control of islet function. By visualizing axons in three dimensions and quantifying axonal densities and contacts within pancreatic islets, we found that, unlike mouse endocrine cells, human endocrine cells are sparsely contacted by autonomic axons. Few parasympathetic cholinergic axons penetrate the human islet, and the invading sympathetic fibers preferentially innervate smooth muscle cells of blood vessels located within the islet. Thus, rather than modulating endocrine cell function directly, sympathetic nerves may regulate hormone secretion in human islets by controlling local blood flow or by acting on islet regions located downstream.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
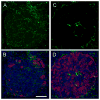
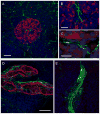
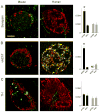
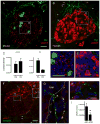
Comment in
-
Islets have a lot of nerve! Or do they?Cell Metab. 2011 Jul 6;14(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.004. Cell Metab. 2011. PMID: 21723498 Free PMC article.
-
Highlights in basic autonomic neurosciences: autonomic control of the counter-regulatory response and glucose homeostasis.Auton Neurosci. 2012 Jul 2;169(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 9. Auton Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22578333 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahrén B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion--implications for health and disease. Diabetologia. 2000;43:393–410. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Ar’Rajab A, Böttcher G, Sundler F, Dunning B. Presence of galanin in human pancreatic nerves and inhibition of insulin secretion from isolated human islets. Cell Tissue Res. 1991;264:263–267. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Holst J. The cephalic insulin response to meal ingestion in humans is dependent on both cholinergic and noncholinergic mechanisms and is important for postprandial glycemia. Diabetes. 2001;50:1030–1038. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Taborsky GJ, Porte DJ. Neuropeptidergic versus cholinergic and adrenergic regulation of islet hormone secretion. Diabetologia. 1986;29:827–836. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Veith R, Taborsky GJ. Sympathetic nerve stimulation versus pancreatic norepinephrine infusion in the dog: 1). Effects on basal release of insulin and glucagon. Endocrinology. 1987;121:323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

