Prone ventilation in the management of infants with acute respiratory distress syndrome after complex cardiac surgery
- PMID: 21724416
- PMCID: PMC9941526
- DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2011.03.179
Prone ventilation in the management of infants with acute respiratory distress syndrome after complex cardiac surgery
Figures
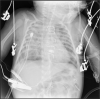

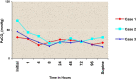
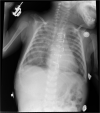
Similar articles
-
Prone Ventilation for Patients with Mild or Moderate Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Jan;17(1):24-29. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201906-456IP. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. PMID: 31532692 Review. No abstract available.
-
Prone ventilation as treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome related to COVID-19.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021 Aug;47(4):1017-1022. doi: 10.1007/s00068-020-01542-7. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 33201268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial hemodynamic effects of prone positioning in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Dec 15;188(12):1428-33. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201303-0593OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 24102072 Clinical Trial.
-
The prone position ventilation (PPV) as an approach in pregnancy with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 May;60(3):574-576. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.03.036. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33966753 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effect of exogenous surfactant in infants suffering acute respiratory distress syndrome after cardiac surgery.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011 Sep;40(3):557-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.01.008. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21371901
References
-
- Fessler H.E., Talmor D.S. Should prone positioning be routinely used for lung protection during mechanical ventilation? Respir Care. 2010;55:88–99. - PubMed
-
- Cui Q., Zhou H., Zhao R., et al. The effects of open lung ventilation on respiratory mechanics and hemodynamics in atelectatic infants after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Int Med Res. 2009;37:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Randolph A.G. Management of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:2447–2454. - PubMed
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1301–1308. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger R.P., Levy M.M., Carlet J.M., et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock; 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

