Iron homeostasis--Achilles' heel of Aspergillus fumigatus?
- PMID: 21724450
- PMCID: PMC3162135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.06.002
Iron homeostasis--Achilles' heel of Aspergillus fumigatus?
Abstract
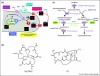
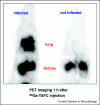
The opportunistic fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus adapts to iron limitation by upregulation of iron uptake mechanisms including siderophore biosynthesis and downregulation of iron-consuming pathways to spare iron. These metabolic changes depend mainly on the transcription factor HapX. Consistent with the crucial role of iron in pathophysiology, genetic inactivation of either HapX or the siderophore system attenuates virulence of A. fumigatus in a murine model of aspergillosis. The differences in iron handling between mammals and fungi might serve to improve therapy and diagnosis of fungal infections.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kaplan C.D., Kaplan J. Iron acquisition and transcriptional regulation. Chem Rev. 2009;109:4536–4552. - PubMed
-
This review comprehensively covers iron uptake, storage and regulation in the fungal modelorganism S. cerevisiae.
-
- Weinberg E.D. Iron availability and infection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790:600–605. - PubMed
-
- Tekaia F., Latge J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus: saprophyte or pathogen? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:385–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

