Specific sequence determinants of miR-15/107 microRNA gene group targets
- PMID: 21724616
- PMCID: PMC3185429
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr532
Specific sequence determinants of miR-15/107 microRNA gene group targets
Abstract
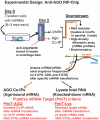
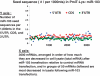
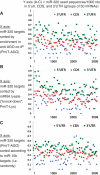
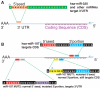
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) target mRNAs in human cells via complex mechanisms that are still incompletely understood. Using anti-Argonaute (anti-AGO) antibody co-immunoprecipitation, followed by microarray analyses and downstream bioinformatics, 'RIP-Chip' experiments enable direct analyses of miRNA targets. RIP-Chip studies (and parallel assessments of total input mRNA) were performed in cultured H4 cells after transfection with miRNAs corresponding to the miR-15/107 gene group (miR-103, miR-107, miR-16 and miR-195), and five control miRNAs. Three biological replicates were run for each condition with a total of 54 separate human Affymetrix Human Gene 1.0 ST array replicates. Computational analyses queried for determinants of miRNA:mRNA binding. The analyses support four major findings: (i) RIP-Chip studies correlated with total input mRNA profiling provides more comprehensive information than using either RIP-Chip or total mRNA profiling alone after miRNA transfections; (ii) new data confirm that miR-107 paralogs target coding sequence (CDS) of mRNA; (iii) biochemical and computational studies indicate that the 3' portion of miRNAs plays a role in guiding miR-103/7 to the CDS of targets; and (iv) there are major sequence-specific targeting differences between miRNAs in terms of CDS versus 3'-untranslated region targeting, and stable AGO association versus mRNA knockdown. Future studies should take this important miRNA-to-miRNA variability into account.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-Argonaute RIP-Chip shows that miRNA transfections alter global patterns of mRNA recruitment to microribonucleoprotein complexes.RNA. 2010 Feb;16(2):394-404. doi: 10.1261/rna.1905910. Epub 2009 Dec 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20042474 Free PMC article.
-
Individual microRNAs (miRNAs) display distinct mRNA targeting "rules".RNA Biol. 2010 May-Jun;7(3):373-80. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.3.11693. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 20421741 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of translationally inhibited and degraded miR-155 targets using RNA-interacting protein-IP.RNA Biol. 2013 Jun;10(6):1018-29. doi: 10.4161/rna.24553. Epub 2013 Apr 15. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23673373 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1;39(16):6845-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr330. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21652644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-107 Targets NSG1 to Regulate Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression through ERK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 29;25(11):5961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892156 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines release the let-7b-mediated suppression of initiation codon recognition during the protein synthesis of EXT2.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 21;6:33549. doi: 10.1038/srep33549. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27650265 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs and estrogen action.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012 May;23(5):223-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22503553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Results from Distinct MicroRNA Target Prediction Tools Enhances the Performance of Analyses.Front Genet. 2017 May 16;8:59. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00059. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28559915 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a/-16 Inhibit Angiogenesis by Targeting the Tie2 Coding Sequence: Therapeutic Potential of a miR-15a/16 Decoy System in Limb Ischemia.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Sep 6;17:49-62. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 17. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31220779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wheeler BM, Heimberg AM, Moy VN, Sperling EA, Holstein TW, Heber S, Peterson KJ. The deep evolution of metazoan microRNAs. Evol. Dev. 2009;11:50–68. - PubMed
-
- Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B, Rigoutsos I. MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature. 2008;455:1124–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

