The diverse functions of Dot1 and H3K79 methylation
- PMID: 21724828
- PMCID: PMC3134078
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2057811
The diverse functions of Dot1 and H3K79 methylation
Abstract
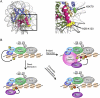
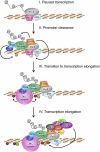
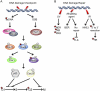
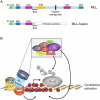
DOT1 (disruptor of telomeric silencing; also called Kmt4) was initially discovered in budding yeast in a genetic screen for genes whose deletion confers defects in telomeric silencing. Since the discovery ∼10 years ago that Dot1 and its mammalian homolog, DOT1L (DOT1-Like), possess histone methyltransferase activity toward histone H3 Lys 79, great progress has been made in characterizing their enzymatic activities and the role of Dot1/DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle regulation, and the DNA damage response. In addition, gene disruption in mice has revealed that mouse DOT1L plays an essential role in embryonic development, hematopoiesis, cardiac function, and the development of leukemia. The involvement of DOT1L enzymatic activity in leukemogenesis driven by a subset of MLL (mixed-lineage leukemia) fusion proteins raises the possibility of targeting DOT1L for therapeutic intervention.
Figures


References
-
- Ayton PM, Cleary ML 2001. Molecular mechanisms of leukemogenesis mediated by MLL fusion proteins. Oncogene 20: 5695–5707 - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K 2007. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129: 823–837 - PubMed
-
- Bitoun E, Oliver PL, Davies KE 2007. The mixed-lineage leukemia fusion partner AF4 stimulates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation and mediates coordinated chromatin remodeling. Hum Mol Genet 16: 92–106 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
