Modification of norfloxacin by a Microbacterium sp. strain isolated from a wastewater treatment plant
- PMID: 21724893
- PMCID: PMC3165385
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00545-11
Modification of norfloxacin by a Microbacterium sp. strain isolated from a wastewater treatment plant
Abstract
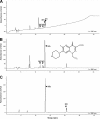
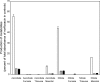
Antimicrobial residues found in municipal wastewater may increase selective pressure on microorganisms for development of resistance, but studies with mixed microbial cultures derived from wastewater have suggested that some bacteria are able to inactivate fluoroquinolones. Medium containing N-phenylpiperazine and inoculated with wastewater was used to enrich fluoroquinolone-modifying bacteria. One bacterial strain isolated from an enrichment culture was identified by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis as a Microbacterium sp. similar to a plant growth-promoting bacterium, Microbacterium azadirachtae (99.70%), and a nematode pathogen, "M. nematophilum" (99.02%). During growth in medium with norfloxacin, this strain produced four metabolites, which were identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses as 8-hydroxynorfloxacin, 6-defluoro-6-hydroxynorfloxacin, desethylene norfloxacin, and N-acetylnorfloxacin. The production of the first three metabolites was enhanced by ascorbic acid and nitrate, but it was inhibited by phosphate, amino acids, mannitol, formate, and thiourea. In contrast, N-acetylnorfloxacin was most abundant in cultures supplemented with amino acids. This is the first report of defluorination and hydroxylation of a fluoroquinolone by an isolated bacterial strain. The results suggest that some bacteria may degrade fluoroquinolones in wastewater to metabolites with less antibacterial activity that could be subject to further degradation by other microorganisms.
Figures

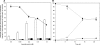


References
-
- Anadón A., et al. 1995. Pharmacokinetics and tissue residues of norfloxacin and its N-desethyl- and oxo-metabolites in healthy pigs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:220–225 - PubMed
-
- Anadón A., Martínez-Larrañaga M. R., Vélez C., Díaz M. J., Bringas P. 1992. Pharmacokinetics of norfloxacin and its N-desethyl- and oxo-metabolites in broiler chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 53:2084–2089 - PubMed
-
- Andersson M. I., MacGowan A. P. 2003. Development of the quinolones. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51(Suppl. S1):1–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

