Phenylacetyl coenzyme A is an effector molecule of the TetR family transcriptional repressor PaaR from Thermus thermophilus HB8
- PMID: 21725002
- PMCID: PMC3165508
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.05203-11
Phenylacetyl coenzyme A is an effector molecule of the TetR family transcriptional repressor PaaR from Thermus thermophilus HB8
Abstract
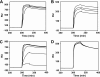
Phenylacetic acid (PAA) is a common intermediate in the catabolic pathways of several structurally related aromatic compounds. It is converted into phenylacetyl coenzyme A (PA-CoA), which is degraded to general metabolites by a set of enzymes. Within the genome of the extremely thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB8, a cluster of genes, including a TetR family transcriptional regulator, may be involved in PAA degradation. The gene product, which we named T. thermophilus PaaR, negatively regulated the expression of the two operons composing the gene cluster in vitro. T. thermophilus PaaR repressed the target gene expression by binding pseudopalindromic sequences, with a consensus sequence of 5'-CNAACGNNCGTTNG-3', surrounding the promoters. PA-CoA is a ligand of PaaR, with a proposed binding stoichiometry of 1:1 protein monomer, and was effective for transcriptional derepression. Thus, PaaR is a functional homolog of PaaX, a GntR transcriptional repressor found in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas strains. A three-dimensional structure of T. thermophilus PaaR was predicted by homology modeling. In the putative structure, PaaR adopts the typical three-dimensional structure of the TetR family proteins, with 10 α-helices. A positively charged surface at the center of the molecule is similar to the acyl-CoA-binding site of another TetR family transcriptional regulator, T. thermophilus FadR, which is involved in fatty acid degradation. The CoA moiety of PA-CoA may bind to the center of the PaaR molecule, in a manner similar to the binding of the CoA moiety of acyl-CoA to FadR.
Figures

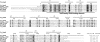

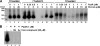
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional repression mediated by a TetR family protein, PfmR, from Thermus thermophilus HB8.J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(17):4630-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.00668-12. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22753056 Free PMC article.
-
TetR-family transcriptional repressor Thermus thermophilus FadR controls fatty acid degradation.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jun;157(Pt 6):1589-1601. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.048017-0. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21349973
-
Involvement of the TetR-Type Regulator PaaR in the Regulation of Pristinamycin I Biosynthesis through an Effect on Precursor Supply in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jun 15;197(12):2062-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.00045-15. Epub 2015 Apr 13. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25868645 Free PMC article.
-
The Escherichia coli FadR transcription factor: Too much of a good thing?Mol Microbiol. 2021 Jun;115(6):1080-1085. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14663. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33283913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FadR, transcriptional co-ordination of metabolic expediency.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Aug;29(4):937-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00917.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9767562 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional repression mediated by a TetR family protein, PfmR, from Thermus thermophilus HB8.J Bacteriol. 2012 Sep;194(17):4630-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.00668-12. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22753056 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the specific regulation of the central pathway for anaerobic degradation of 3-methylbenzoate.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8;290(19):12165-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.637074. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25795774 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of preferred DNA-binding sites for the Thermus thermophilus transcriptional regulator FadR.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 13;12(9):e0184796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184796. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28902898 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Preferred DNA-Binding Sites for the Thermus thermophilus HB8 Transcriptional Regulator TTHA0973.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 7;20(13):3336. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133336. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31284644 Free PMC article.
-
The TetR family of regulators.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013 Sep;77(3):440-75. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00018-13. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24006471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agari Y., Agari K., Sakamoto K., Kuramitsu S., Shinkai A. 2011. TetR family transcriptional repressor Thermus thermophilusFadR controls fatty acid degradation. Microbiology 157:1589–1601 - PubMed
-
- DiRusso C. C., Heimert T. L., Metzger A. K. 1992. Characterization of FadR, a global transcriptional regulator of fatty acid metabolism in Escherichia coli. Interaction with the fadBpromoter is prevented by long chain fatty acyl coenzyme A. J. Biol. Chem. 267:8685–8691 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

