A novel toxin regulator, the CPE1446-CPE1447 protein heteromeric complex, controls toxin genes in Clostridium perfringens
- PMID: 21725013
- PMCID: PMC3165525
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00262-11
A novel toxin regulator, the CPE1446-CPE1447 protein heteromeric complex, controls toxin genes in Clostridium perfringens
Abstract
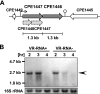
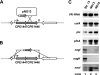
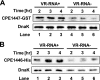
Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore-forming bacterium that is widespread in environmental soil and sewage, as well as in animal intestines. It is also a causative agent of diseases in humans and other animals, and it produces numerous extracellular enzymes and toxins. Although these toxins have been characterized in detail, regulators of toxin genes are less well understood. The present study identified CPE1447 and CPE1446 as novel regulators of toxin gene expression. CPE1447 and CPE1446 are cotranscribed as an operon, and the encoded proteins have a helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif at the N termini of their amino acid sequences, suggesting that CPE1447 and CPE1446 control the target genes as transcriptional regulators. The expression of several genes encoding toxins was changed in both a CPE1446 mutant and a CPE1447-CPE1446 deletion mutant. Complementation of CPE1446 and CPE1447 revealed that CPE1447 and CPE1446 coordinately regulate their target genes. CPE1447 protein was coprecipitated with His-tagged CPE1446 protein, indicating that the CPE1447 and CPE1446 proteins form a stable complex in C. perfringens under their native conditions. Although the small RNA that regulates several genes under the VirR/VirS two-component system (VR-RNA) positively affected CPE1447-CPE1446 mRNA expression, it did not control expression of the CPE1447-CPE1446 regulon, demonstrating that CPE1447 and CPE1446 regulate a different set of toxin genes from the VirR/VirS-VR-RNA cascade.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifying the Basis for VirS/VirR Two-Component Regulatory System Control of Clostridium perfringens Beta-Toxin Production.J Bacteriol. 2021 Aug 20;203(18):e0027921. doi: 10.1128/JB.00279-21. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34228498 Free PMC article.
-
The virR/virS locus regulates the transcription of genes encoding extracellular toxin production in Clostridium perfringens.J Bacteriol. 1996 May;178(9):2514-20. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.9.2514-2520.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8626316 Free PMC article.
-
The VirR/VirS regulatory cascade affects transcription of plasmid-encoded putative virulence genes in Clostridium perfringens strain 13.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003 May 16;222(1):137-41. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00255-6. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12757957
-
Gene regulation by the VirS/VirR system in Clostridium perfringens.Anaerobe. 2016 Oct;41:5-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Anaerobe. 2016. PMID: 27296833 Review.
-
Regulation of toxin gene expression in Clostridium perfringens.Res Microbiol. 2015 May;166(4):280-9. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Res Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25303832 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel pore-forming toxin in type A Clostridium perfringens is associated with both fatal canine hemorrhagic gastroenteritis and fatal foal necrotizing enterocolitis.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 8;10(4):e0122684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122684. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25853427 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Genomic Analyses and Toxinotyping of Clostridium perfringens Implicated in Foodborne Outbreaks in France.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 17;10:777. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00777. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31057505 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing and analysis of a type A Clostridium perfringens isolate from a case of bovine clostridial abomasitis.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032271. Epub 2012 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22412860 Free PMC article.
-
Sialidases From Clostridium perfringens and Their Inhibitors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 10;9:462. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00462. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31998664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small regulatory RNAs from low-GC Gram-positive bacteria.RNA Biol. 2014;11(5):443-56. doi: 10.4161/rna.28036. Epub 2014 Feb 10. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe K., Obana N., Nakamura K. 2010. Effects of depletion of RNA-binding protein Tex on the expression of toxin genes in Clostridium perfringens. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74:1564–1571 - PubMed
-
- Awad M. M., Bryant A. E., Stevens D. L., Rood J. I. 1995. Virulence studies on chromosomal alpha-toxin and theta-toxin mutants constructed by allelic exchange provide genetic evidence for the essential role of alpha-toxin in Clostridium perfringens-mediated gas gangrene. Mol. Microbiol. 15:191–202 - PubMed
-
- Banu S., et al. 2000. Identification of novel VirR/VirS-regulated genes in Clostridium perfringens. Mol. Microbiol. 35:854–864 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

