Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging-induced degradation of HaloTag fusion proteins
- PMID: 21725302
- PMCID: PMC3139752
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.597
Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging-induced degradation of HaloTag fusion proteins
Abstract
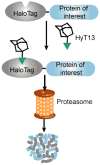
The ability to regulate any protein of interest in living systems with small molecules remains a challenge. We hypothesized that appending a hydrophobic moiety to the surface of a protein would mimic the partially denatured state of the protein, thus engaging the cellular quality control machinery to induce its proteasomal degradation. We designed and synthesized bifunctional small molecules to bind a bacterial dehalogenase (the HaloTag protein) and present a hydrophobic group on its surface. Hydrophobic tagging of the HaloTag protein with an adamantyl moiety induced the degradation of cytosolic, isoprenylated and transmembrane HaloTag fusion proteins in cell culture. We demonstrated the in vivo utility of hydrophobic tagging by degrading proteins expressed in zebrafish embryos and by inhibiting Hras1(G12V)-driven tumor progression in mice. Therefore, hydrophobic tagging of HaloTag fusion proteins affords small-molecule control over any protein of interest, making it an ideal system for validating potential drug targets in disease models.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Regulation through degradation.Nat Methods. 2011 Sep;8(9):711. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1686. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21985003
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/123111427
- PubChem-Substance/123111428
- PubChem-Substance/123111429
- PubChem-Substance/123111430
- PubChem-Substance/123111431
- PubChem-Substance/123111432
- PubChem-Substance/123111433
- PubChem-Substance/123111434
- PubChem-Substance/123111435
- PubChem-Substance/123111436
- PubChem-Substance/123111437
- PubChem-Substance/123111438
- PubChem-Substance/123111439
- PubChem-Substance/123111440
- PubChem-Substance/123111441
- PubChem-Substance/123111442
- PubChem-Substance/123111443
- PubChem-Substance/123111444
- PubChem-Substance/123111445
- PubChem-Substance/123111446
- PubChem-Substance/123111447
- PubChem-Substance/123111448
- PubChem-Substance/123111449
- PubChem-Substance/123111450
- PubChem-Substance/123111451
- PubChem-Substance/123111452
- PubChem-Substance/123111453
- PubChem-Substance/123111454
- PubChem-Substance/123111455
- PubChem-Substance/123111458
- PubChem-Substance/123111459
- PubChem-Substance/123111460
- PubChem-Substance/123111461
- PubChem-Substance/123111462
- PubChem-Substance/123111463
- PubChem-Substance/123111464
- PubChem-Substance/123111465
- PubChem-Substance/123111466
- PubChem-Substance/123111467
- PubChem-Substance/123111468
- PubChem-Substance/123111469
- PubChem-Substance/123111470
- PubChem-Substance/123111471
- PubChem-Substance/123111472
- PubChem-Substance/123111473
- PubChem-Substance/123111474
- PubChem-Substance/123111475
- PubChem-Substance/123111476
- PubChem-Substance/123111477
- PubChem-Substance/123111478
- PubChem-Substance/123111479
- PubChem-Substance/123111480
- PubChem-Substance/123111481
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

