Fluorescence-based evaluation of shRNA efficacy
- PMID: 21726522
- PMCID: PMC3143307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2011.06.008
Fluorescence-based evaluation of shRNA efficacy
Abstract
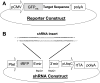
RNA interference is a cellular mechanism regulating levels of mRNAs. It has been widely exploited to knock down specific protein targets. The selected interfering RNA sequence greatly influences its ability to knock down the target. Here we present a method for constructing multiple testing plasmids which express small hairpin RNAs (shRNA) targeting different regions of an mRNA. A simple fluorescence test in cultured cells allows convenient evaluation of mRNA knockdown by many different shRNAs on 96-well plates. We show that software predicted shRNAs have varying efficacies and only 2 of the 7 tested shRNAs significantly knocked down their targets.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Paddison PJ, Silva JM, Conklin DS, Schlabach M, Li M, Aruleba S, Balija V, O’Shaughnessy A, Gnoj L, Scobie K, Chang K, Westbrook T, Cleary M, Sachidanandam R, McCombie WR, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ. A resource for large-scale RNA-interference-based screens in mammals. Nature. 2004;428:427–31. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

