Accuracy of a novel system for oxygen delivery to small children
- PMID: 21727103
- PMCID: PMC3387857
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-3745
Accuracy of a novel system for oxygen delivery to small children
Abstract
Objective: Oxygen therapy for infants and small children in developing countries is often not available. Entrainment devices may provide an accurate and precise concentration of oxygen when used at the flow rates appropriate for infants and small children.
Methods: A continuously adjustable entrainment device was tested to determine the concentrations and flows of oxygen delivered by using low inlet flow rates suitable for therapy for infants and small children and 3 distinct oxygen delivery systems that varied in their resistive load.
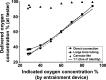
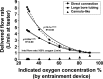
Results: The use of long and large bore, low resistance tubing (similar to a mask) resulted in the delivery of oxygen concentrations that tracked closely (accurate and precise) to values indicated by the entrainment device. The directly connected system with lower resistance (similar to a hood) produced a similar profile of concentrations and flow rates to the large bore tubing but with even greater accuracy. The use of a long and narrow tubing with higher resistance (similar to a cannula) did not deliver accurate oxygen concentrations. In fact, this high-resistance system failed to work as intended, and instead of entraining air, a large proportion (sometimes >50%) of the oxygen delivered to the entrainment device was ejected through its vents.
Conclusions: Entrainment devices can deliver accurate oxygen concentrations at low flow rates if used with low resistance delivery systems; however, entrainment devices are not suitable for use with high resistance delivery systems such as a standard nasal cannula.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The efficacy of noncontact oxygen delivery methods.Pediatrics. 2002 Nov;110(5):964-7. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.5.964. Pediatrics. 2002. PMID: 12415037
-
The application of a surgical face mask over different oxygen delivery devices; a crossover study of measured end-tidal oxygen concentrations.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Mar 7;22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01602-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35255824 Free PMC article.
-
Concentrations of oxygen delivered by air entrainment oxygen masks.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1985 Nov;67(6):366-7. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1985. PMID: 4073765 Free PMC article.
-
High-flow oxygen administration by nasal cannula for adult and perinatal patients.Respir Care. 2013 Jan;58(1):98-122. doi: 10.4187/respcare.01941. Respir Care. 2013. PMID: 23271822 Review.
-
Oxygen delivery to children with hypoxaemia in small hospitals in developing countries.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001 Jun;5(6):527-32. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001. PMID: 11409579 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of an innovative low flow oxygen blender system for global access.Front Pediatr. 2022 Sep 12;10:981821. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.981821. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36186642 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen management among infants in neonatal units in sub-Saharan Africa: a cross-sectional survey.J Perinatol. 2021 Nov;41(11):2631-2638. doi: 10.1038/s41372-021-01040-7. Epub 2021 Mar 26. J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 33772113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Åhman E, Zupan J. Neonatal and Perinatal Mortality: Country, Regional and Global Estimates 2004. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press; 2007
-
- Duke T, Wandi F, Jonathan M, Matai S, Kaupa M, Saavu M, Subhi R, Peel D. Improved oxygen systems for childhood pneumonia: a multihospital effectiveness study in Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 2008;372(9646):1328–1333 - PubMed
-
- Wardlaw TM, Johansson EW, Hodge M. Pneumonia: The Forgotten Killer of Children. New York, NY; Geneva, Switzerland: United Nations Children's Fund/World Health Organization; 2006
-
- Chatburn RL, Williams TJ. Performance of 4 portable oxygen concentrators. Respir Care. 2010;55(4):433–442 - PubMed
-
- Mokuolu OA, Ajayi OA. Use of an oxygen concentrator in a Nigerian neonatal unit: economic implications and reliability. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2002;22(3):209–212 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

