Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 21727191
- PMCID: PMC3136685
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20110551
Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
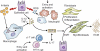
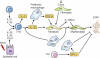
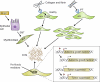
Pulmonary fibrosis is a highly heterogeneous and lethal pathological process with limited therapeutic options. Although research on the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis has frequently focused on the mechanisms that regulate the proliferation, activation, and differentiation of collagen-secreting myofibroblasts, recent studies have identified new pathogenic mechanisms that are critically involved in the initiation and progression of fibrosis in a variety of settings. A more detailed and integrated understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis could help pave the way for effective therapeutics for this devastating and complex disease.
Figures

References
-
- Asangani I.A., Rasheed S.A., Nikolova D.A., Leupold J.H., Colburn N.H., Post S., Allgayer H. 2008. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136 10.1038/sj.onc.1210856 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atabai K., Jame S., Azhar N., Kuo A., Lam M., McKleroy W., Dehart G., Rahman S., Xia D.D., Melton A.C., et al. 2009. Mfge8 diminishes the severity of tissue fibrosis in mice by binding and targeting collagen for uptake by macrophages. J. Clin. Invest. 119:3713–3722 10.1172/JCI40053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bauman K.A., Wettlaufer S.H., Okunishi K., Vannella K.M., Stoolman J.S., Huang S.K., Courey A.J., White E.S., Hogaboam C.M., Simon R.H., et al. 2010. The antifibrotic effects of plasminogen activation occur via prostaglandin E2 synthesis in humans and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 120:1950–1960 10.1172/JCI38369 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

