Immunomodulator expression in trophoblasts from the feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)-infected cat
- PMID: 21729293
- PMCID: PMC3152912
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-336
Immunomodulator expression in trophoblasts from the feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV)-infected cat
Abstract
Background: FIV infection frequently compromises pregnancy under experimental conditions and is accompanied by aberrant expression of some placental cytokines. Trophoblasts produce numerous immunomodulators that play a role in placental development and pregnancy maintenance. We hypothesized that FIV infection may cause dysregulation of trophoblast immunomodulator expression, and aberrant expression of these molecules may potentiate inflammation and compromise pregnancy. The purpose of this project was to evaluate the expression of representative pro-(TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12p35, IL-12p40, IL-18, and GM-CSF) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10); CD134, a secondary co-stimulatory molecule expressed on activated T cells (FIV primary receptor); the chemokine receptor CXCR4 (FIV co-receptor); SDF-1α, the chemokine ligand to CXCR4; and FIV gag in trophoblasts from early-and late-term pregnancy.
Methods: We used an anti-cytokeratin antibody in immunohistochemistry to identify trophoblasts selectively, collected these cells using laser capture microdissection, and extracted total RNA from the captured cell populations. Real time, reverse transcription-PCR was used to quantify gene expression.
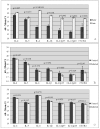
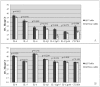
Results: We detected IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12p35, IL-12p40, and CXCR4 in trophoblasts from early-and late-term pregnancy. Expression of cytokines increased from early to late pregnancy in normal tissues. A clear, pro-inflammatory microenvironment was not evident in trophoblasts from FIV-infected queens at either stage of pregnancy. Reproductive failure was accompanied by down-regulation of both pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines. CD134 was not detected in trophoblasts, and FIV gag was detected in only one of ten trophoblast specimens collected from FIV-infected queens.
Conclusion: Feline trophoblasts express an array of pro-and anti-inflammatory immunomodulators whose expression increases from early to late pregnancy in normal tissues. Non-viable pregnancies were associated with decreased expression of immunomodulators which regulate trophoblast invasion in other species. The detection of FIV RNA in trophoblasts was rare, suggesting that the high rate of reproductive failure in FIV-infected queens was not a direct result of viral replication in trophoblasts. The influence of placental immune cells on trophoblast function and pregnancy maintenance in the FIV-infected cat requires additional study.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett WA, Lagoo-Deenadayalan S, Stopple JA, Barber WH, Hale E, Brackin MN, Cowan BD. Cytokine expression by first-trimester human chorionic villi. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1998;40:309–318. - PubMed
-
- Robertson SA, Seamark RF, Guilbert LJ, Wegmann TG. The role of cytokines in gestation. Crit Rev Immunol. 1994;14:239–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

